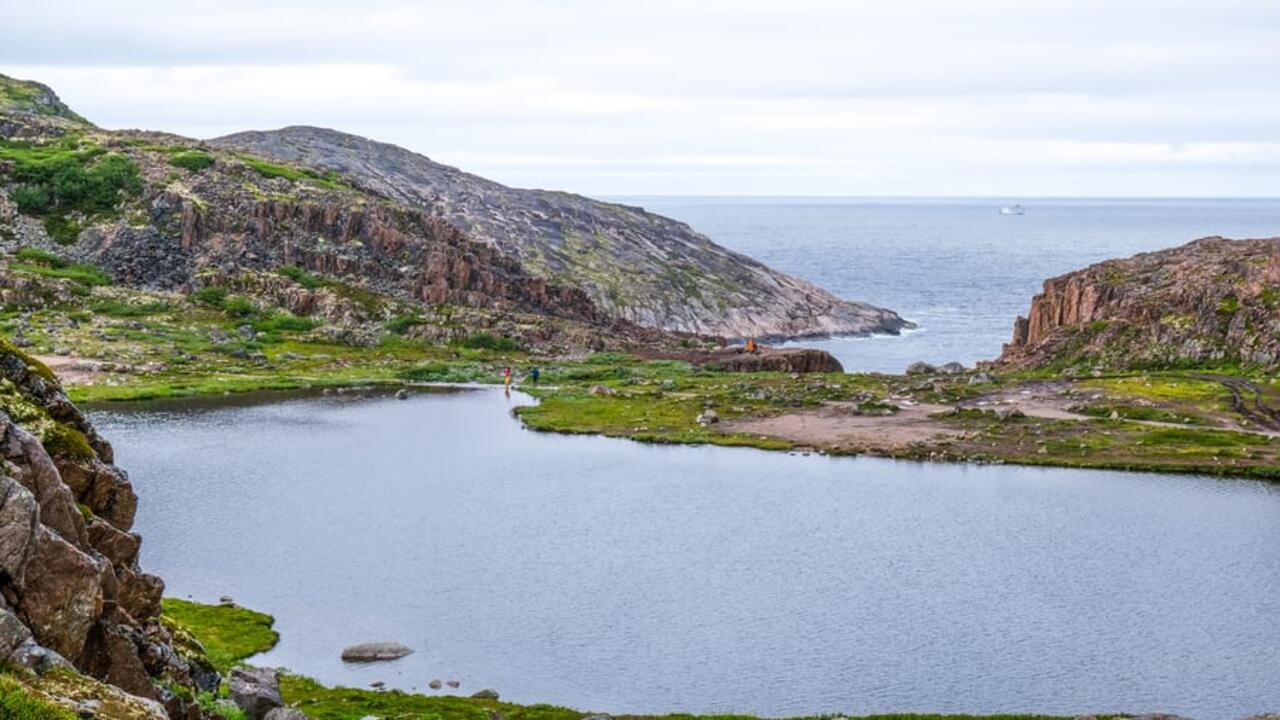

Evidence of accelerated climate change seen in Labrador mountain range
Climate change is accelerating shrub growth across many northern regions, which has important consequences for people and wildlife there.

Climate change is accelerating shrub growth across many northern regions, which has important consequences for people and wildlife there.
By Media RelationsClimate change is accelerating shrub growth across many northern regions, which has important consequences for people and wildlife who live there.
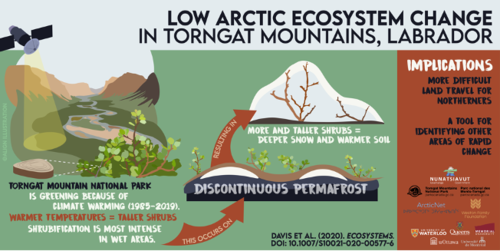
A new study led by Emma Davis, a University of Waterloo postdoctoral fellow, examines rapid shrub expansion in Torngats Mountains National Park. The changes were first detected by Inuit elders, prompting Davis’ interdisciplinary team of researchers to determine how climate change is impacting Nunatsiavut, in northern Labrador.
“To understand why shrub growth is accelerating we needed data, expertise and knowledge from many different disciplines and communities,” said Davis. “Climate change in the Western Arctic has been studied extensively, our approach was to bring together a diversity of people to paint a clearer picture of where arctic climate change is going.”
Traditional knowledge was a motivation for the work, now published in Ecosystems. The paper includes on-the-ground expertise from government partners including Darroch Whitaker an ecosystem scientist with Parks Canada and a co-author on the report.
“Rapid shrub expansion was first brought to our attention by Inuit elders and was of concern to them because shrubs can make travel on the land more difficult, provide cover that helps bears hide, and changes the way they can use the land,” said Whitaker.
The study is remarkable because of the length of time of the long-term collaboration between university researchers and Parks Canada staff.
“The report was done in consultation with the park’s Cooperative Management Board, and helps us better understand how this profound environmental change is affecting the ecological integrity of the park and the lives of Inuit in the region.”
A full version of the report, Plant–Environment Interactions in the Low Arctic Torngat Mountains of Labrador, can be found here.

Read more
The Future Cities Institute founded by CAIVAN will bring together leading minds from across sectors to solve the most challenging and urgent issues facing global cities.

Read more
The gift comes from two Waterloo alumni with passion and drive to have transformative impact

Read more
University of Waterloo and leading real estate developer The Caivan Group launch the Future Cities Institute
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.