If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
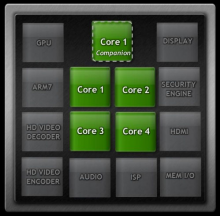
A long-time frontrunner in the desktop graphics market, Nvidia Corporation, located in Santa Clara, California, has recently expanded their product line to feature mobile devices. The Tegra 3 system-on-a-chip (SoC) integrates Nvidia’s latest central processing, graphics processing, and memory controller hardware into a single chip. Unlike typical desktop processors, mobile processors are limited by a device’s battery and the energy it is capable of delivering. Providing the right balance between processing capability and battery life requires the optimization of hardware-kernel interaction, as well as the processor’s reaction to the demands of software.
Sai Charan Gurrappadi, a fourth-year Mechatronics Engineering student, was asked to analyze the central processor usage and its impact on power consumption and battery life.
The teaching objectives of this case study are to introduce the basics of power within an integrated circuit, the power management as specific to the Tegra 3 architecture, to provide an explanation for current power management policies and to necessitate the development of a suitable replacement/addition to current power policy in order to reduce power consumption. This case study can be used as effective material for Digital Hardware Systems (ECE 327).
If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
Contact Waterloo Cases in Design Engineering
Steve Lambert
Tel: (519) 888-4728
Email: steve@uwaterloo.ca
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.