To examine a new model of DSF systems with integrated renewable sources using Computational Fluid Dynamics
Energy & Environment
Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)Description
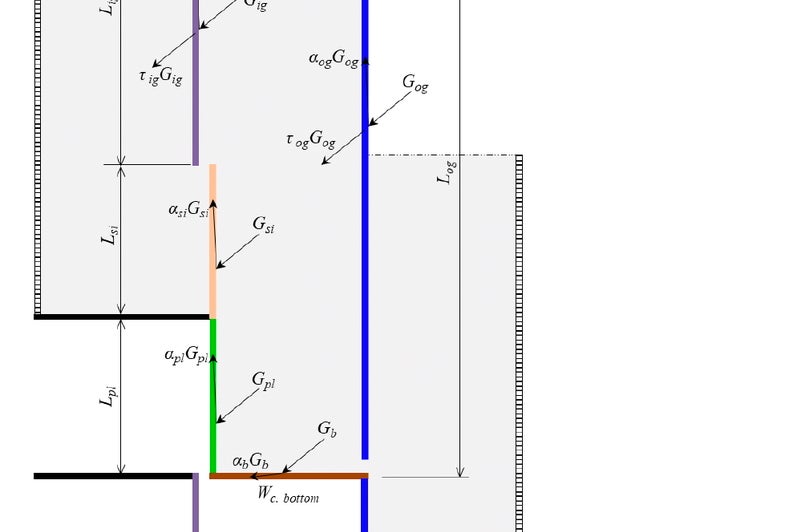
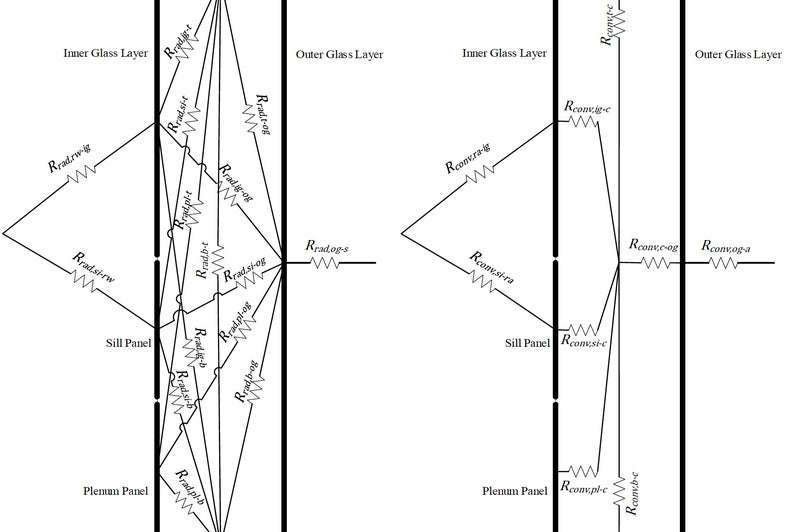
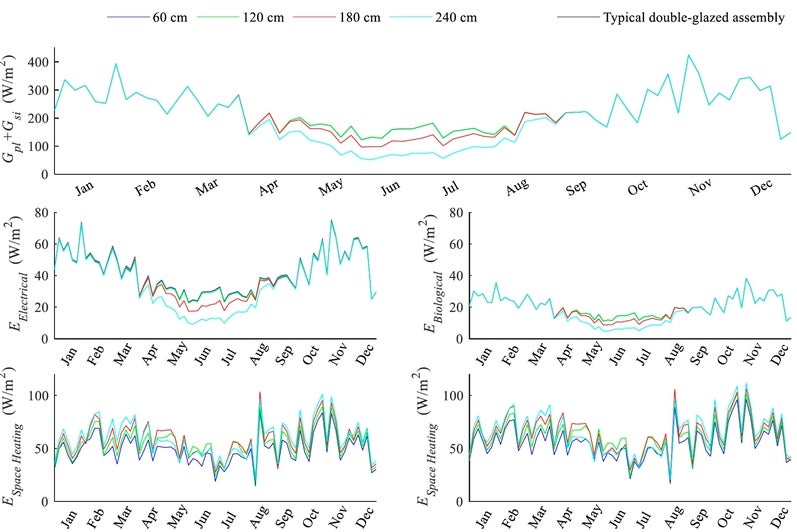
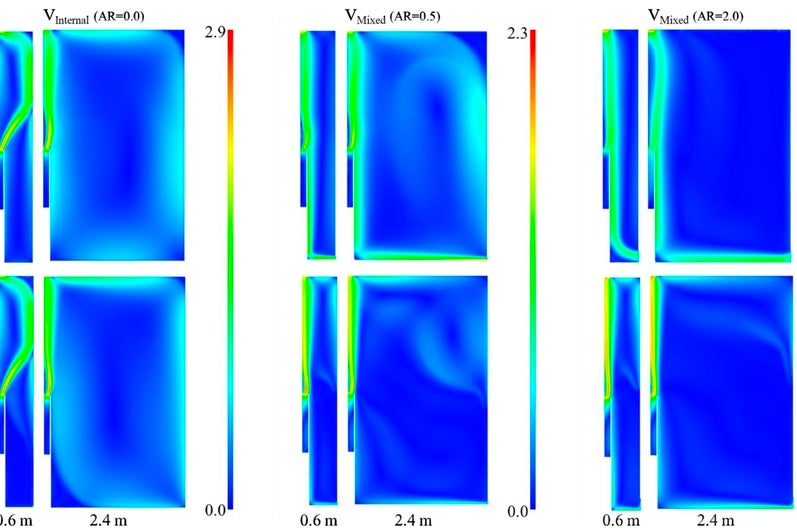
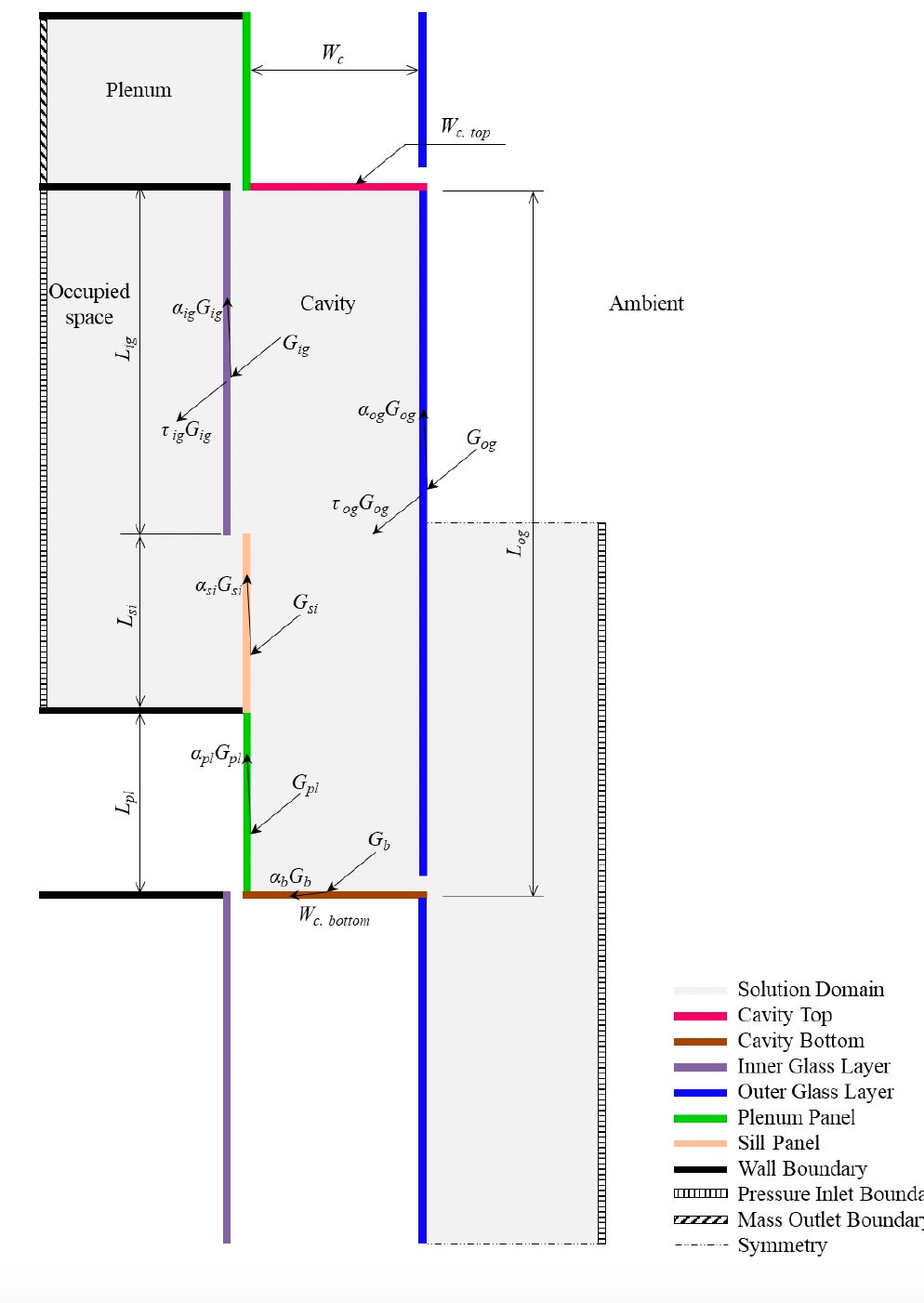
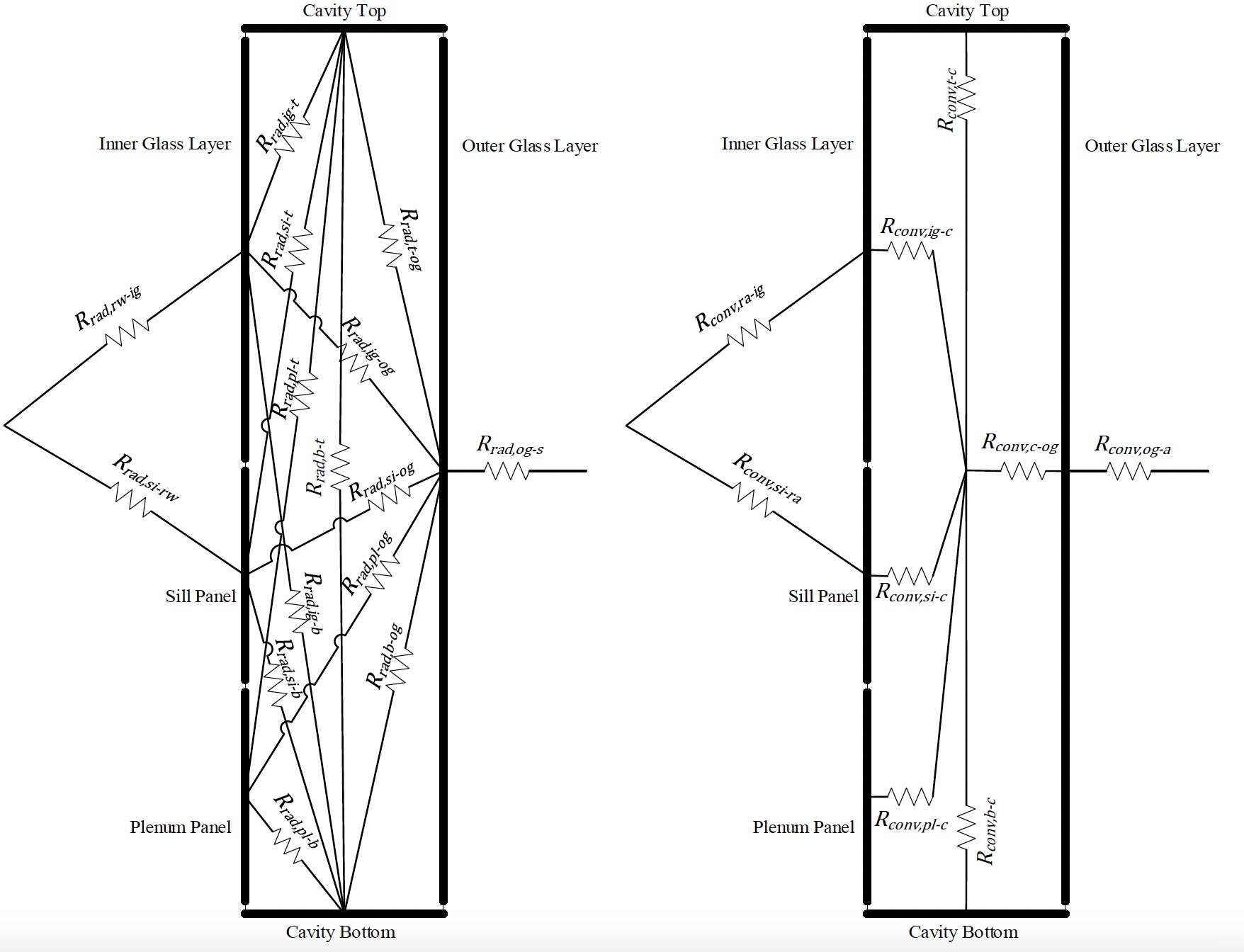
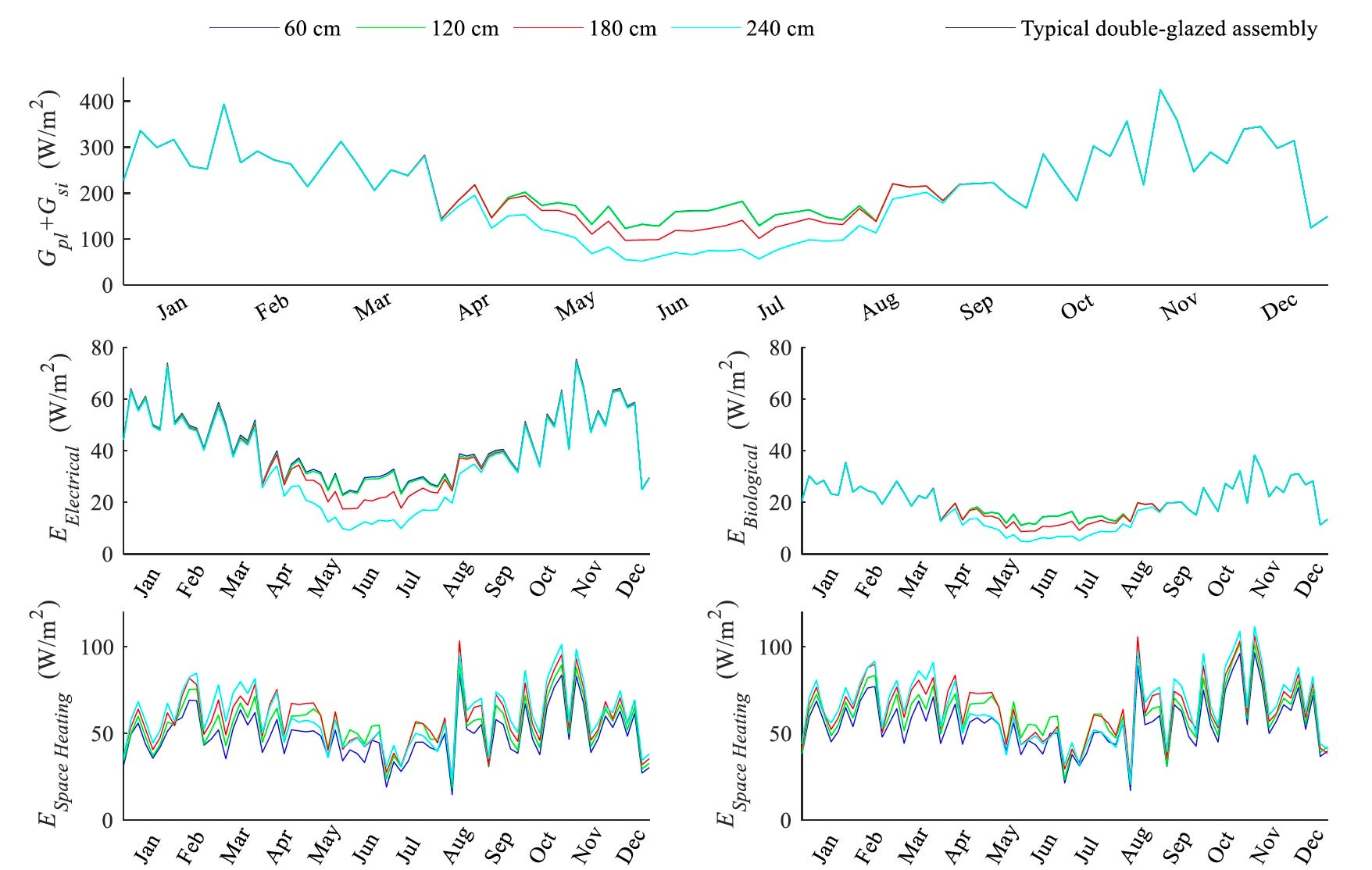
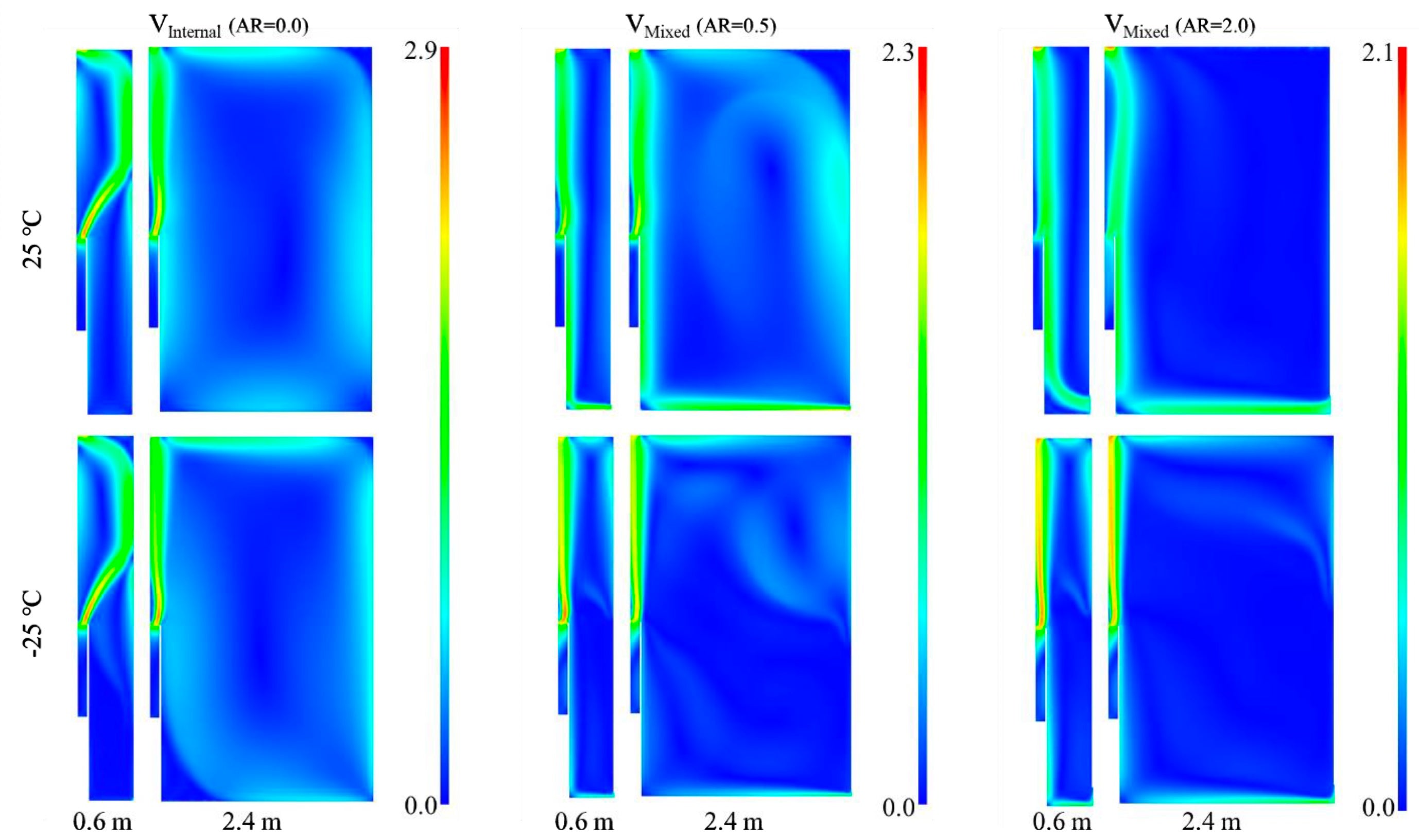
Double-skin façades often rely on proper cavity design, which unleashes a significant potential for inhabitation and renewable energy integration in cold climates. A co-model between Matlab and Ansys Fluent was developed to investigate the performance of a new typology for such façades. The model was validated against experimental measurements where the average temperature deviation was 1.9 °C. For the renewable energy source, the system utilized PVs and microalgae modules which were brought in contact with the occupied space in order to counter the heat loss to the cold ambient. Results showed the flow of heat transfer was reversed from 82.1 W/m2 loss to the surrounding to 35.7 W/m2 gain into the occupied space. The project recommended utilizing adjustable external air vents that can be regulated depending on the ambient temperature and the personal occupancy level in the cavity whenever its size fits.