Discover Symbiosis Lab's cutting-edge projects
In the three thematic areas of Energy & Environment, Technology & Design, and Materials Science & Engineering, we have deep knowledge in a number of specific applications. Learn more about our strategies and solutions for every problem. Our capabilities coupled with emerging technologies are powerful for improving decision making and finding solutions to toughest challenges.
Aerial Building Audits
This project utilizes UAVs for building envelope audits, incorporating thermal, LiDAR, RGB, and hyperspectral sensors. Tools like Metashape, Revit, EnergyPlus, and custom Python/C++ code enable 3D modeling, analysis, visualization, simulation and energy performance evaluation.
Snow Cover Detection on PV
This project develops deep learning and image processing methods to assess snow impact on photovoltaic panels, enabling remote monitoring, accurate performance estimation, and improved energy production efficiency in cold climates through per-pixel analysis and digital photography.
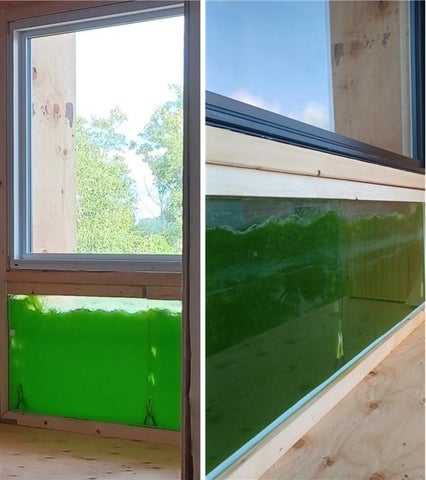
Algal Bioreactive Façades
This project optimizes façade-integrated microalgae photobioreactors to enhance building performance, reduce energy demand, improve thermal comfort, and generate biomass and thermal energy, using multiple optimization techniques, shading analysis, and hourly thermal simulations.
Efficient Façade Forms
This project optimizes façade design for resilient solar harvesting using the Hooke-Jeeves algorithm, highlighting its efficiency and limitations, and shows that free-form façades enhance irradiation and renewable energy generation, with south-facing orientations achieving the highest performance.
Solar Radiation Modelling
This project develops and validates new trigonometric shading models for diverse urban environments, outperforming existing techniques and showing that free-form façades and south-facing orientations significantly enhance solar radiation capture compared to flat façades.
Effects of Welding Near Concrete
This project investigates welding thermal effects on metal components near concrete in nuclear reactors, aiming to minimize thermal stresses, comply with standard guidelines, and improve the safety and efficiency of welding operations in nuclear facilities.
PCM-Integrated Cooling
This project optimizes thermally active building systems integrating solar technologies, and multiple heat sources, achieving energy savings, reduced costs and emissions, and enhanced thermal comfort, demonstrating their potential for sustainable performance across diverse climate conditions.
Optimizing District Heating
This project develops optimization techniques and peer-to-peer heat trading to improve district heating efficiency and sustainability, demonstrating significant cost and emission reductions, enhanced flexibility with optimized storage, and scalable renewable-powered solutions for sustainable urban energy systems.
PV Water Cooling
This project integrates an optimization method and energy flow model to reduce PV temperature and boost power generation, achieving significant cost savings, and rapid payback by optimizing water flow, pipe spacing, and tilt angle.
Triple-Function Solar Collector
This project develops advanced solar collector designs, including a triple-function collector combining hot water, air, and electricity generation with high energy and exergy efficiencies, and optimized cavity receivers, highlighting their potential for sustainable residential and commercial energy applications.
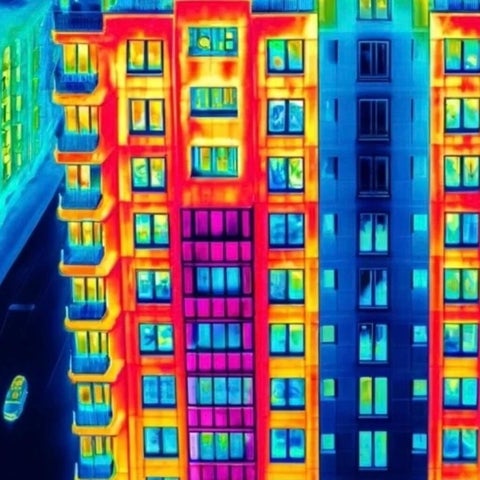
Thermal Imaging for Buildings
This project develops an autonomous façade heat loss inspection method using thermal imaging, YOLOv7 deep learning, and heat flow modeling, accurately detecting anomalies, quantifying heat loss, and identifying critical areas, enhancing monitoring in cold-climate buildings.
CFD-Façade Modelling
This project develops and validates a co-model between Matlab and Ansys Fluent to optimize double-skin façades with PVs and microalgae, reversing heat loss into heat gain and enhancing renewable integration and thermal performance in cold climates.
ML for Renewable Energy
This project develops a deep learning method to detect snow coverage on PV panels, improving real-time energy loss estimation, achieving high prediction accuracy, and enabling timely snow removal to maximize solar energy conversion in cold regions.
Shadow Pattern on PV
This project develops deep learning and Hough Transform methods to detect regular and irregular shading on PV arrays, improving shadow identification, enhancing energy yield predictions, and enabling accurate segmentation without requiring a specific PV image dataset.
ML-Optimization Procedures
This project applies Neural Networks to optimize building-integrated photobioreactors, significantly reducing computational time, enhancing efficiency, and addressing limitations of traditional meta-heuristic methods while achieving optimal bioenergy generation throughout the year.
Dynamic Façades Mechatronics
This project evaluates mechatronic dynamic façades using PID and machine learning controllers, highlighting the importance of adaptive light distribution for visual comfort and energy optimization, and emphasizing the role of meteorological data for seasonal performance analysis.
Chlorella on Ceramics
This project investigates microalgae growth on ceramic-based porous substrate bioreactors, analyzing the effects of surface texture, nutrient availability, and environmental exposure using vegetation indices, color kinetics, and microscopy to optimize cultivation efficiency.
Ventilation in Façade Design
This project develops a neural network-aided thermal model to evaluate Double-Skin Façades, demonstrating their effectiveness in reducing heat loss and gain, enhancing thermal comfort, and optimizing façade performance under various ventilation conditions in cold regions.
Microalgae Chemical Kinetics
This project models microalgae photobioreactors integrated into double-skin façades, using kinetics, shading analysis, and optimization to maximize biomass productivity, validate performance with RGB monitoring, and demonstrate adaptability across diverse cold-climate conditions.
Adaptive Reuse-Energy
This project develops a neural network-based framework to assess adaptive reuse strategies, analyzing building expansions and façade glazing, and evaluating their impact on energy consumption, production, and daylighting to support net-zero energy goals in existing buildings.
3D Grid Façade Subtraction
This project develops a parametric workflow to generate 3D grid-based façades, integrating photovoltaic panels and vision glass, and evaluates their impact on daylighting and renewable energy production compared to conventional straight façades.
Mycelium Wall Systems
Mycelium composites were investigated for wall systems through phased experiments, iterative digital modeling, and prototype fabrication. Results showed comparable assembly ease and thermal insulation performance to typical prefabricated walls, highlighting sustainable architectural applications.
Robotic WAAM Steel Joints
This project explores additive manufacturing for developing optimized structural joints, using small-scale prototypes and robotic Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing to test integrity, efficiency, and aesthetics, enabling innovative large-scale architectural designs with improved accuracy and manufacturability.
ML-aided Energy Efficiency
This project applies machine learning and computational analysis to optimize urban typologies, evaluating building forms, energy balance, and environmental properties, and performing sensitivity analysis to guide efficient, integrated urban design under key constraints.
Airborne PM2.5 Filtration
This project evaluates a novel air filtration technology for reducing PM2.5 concentrations in office environments, demonstrating its effectiveness under varying occupancy conditions and improving indoor air quality by enhancing particle removal through inelastic collisions.
CFD-ML Wind Modelling
This project develops a framework combining CFD and machine learning to analyze and predict urban wind behavior, automating 3D urban form generation and assessing the impact of building and street parameters on microclimate and wind velocity.
Building Integrated PV
This project optimizes building-integrated PV systems, analyzing building form, orientation, and shading effects, and develops mathematical models to enhance energy efficiency, achieve net-zero goals, and maximize solar energy performance through form and tilt optimization.
Radiosity Glass Wall
This project develops a mathematical model to analyze heat transfer in a novel insulating glass assembly with glass spheres, optimizing daylight transmittance, minimizing solar heat gain, and comparing performance with conventional double and triple-glazed units.
Lighting in Surplus Energy Offices
This project examines lighting design strategies and technologies in the Masdar Headquarters, optimizing daylighting and electric lighting systems, integrating advanced controls, and emphasizing human-centered design to achieve net-positive energy performance and sustainable indoor visual comfort.
Double Skin Façades
This project develops workflows for evaluating Double Skin Façades, integrating parametric simulations, heat transfer modeling, finite element analysis, and optimization techniques to enhance energy efficiency, daylighting, and thermal performance in cold-climate building designs.
Materiality & Environmental Impact
This project examines the environmental and health impacts of synthetic materials, highlighting the limited testing of chemicals, their associated risks, and the need for sustainable design and manufacturing practices to minimize negative effects on humans and ecosystems.
Flux Transfer with Glare Criterion
This project develops a mathematical glare index to guide façade sizing, balancing visual comfort, occupant health, and wellbeing, and complements existing daylighting standards by addressing both discomfort glare and non-visual stimulation in building design.
Radiance-Matlab Interface
This project uses Radiance-Matlab visualizations to optimize daylighting in offices, evaluating lighting indices, illuminance, and exposure duration, and analyzing the effects of façade orientation, seasons, glazing, and task conditions on visual comfort and circadian rhythm.
Urban Density & Life Expectancy
This project investigates the relationship between urban density, energy use, and life expectancy, examining how city design, daily behaviors, and resource efficiency influence health, wellbeing, and sustainability, while questioning common perceptions of dense urban environments.
Visual Comfort in Transient Spaces
This project investigates visual discomfort at building entryways caused by abrupt daylight transitions, evaluating design features like trellises, overhangs, and fins, and assessing their impact on luminance ratios to improve occupant visual comfort during transitions.
Building Matrix
This project uses site analysis to evaluate building density and land use, identifying optimal configurations for multiple façade typologies while considering constraints, area allowances, and permutations to enhance overall urban performance and design efficiency.
Urban Decarbonization
This project develops a methodology to reduce urban carbon emissions while enhancing vibrancy, combining systematic documentation and parametric modeling to assess buildings’ performance across energy, carbon, water, and systems integration, enabling efficient auditing and improvement strategies.
BEEnow Certification
This project develops a voluntary certification program for architecture schools to promote sustainable, low-energy design education, establishing a flexible credit-based system, validated through faculty and student feedback, and supported by the BEEnow initiative for broader adoption.
Data Visualization
This project enhances architectural pedagogy by developing methods for effective data visualization, helping students interpret complex, multi-layered datasets from site analysis, and enabling clearer understanding and application of design problems and patterns in their projects.
Carbon Neutral Buildings
This project integrates architectural, structural, and mechanical design with construction and facilities management to develop cost-effective, carbon-neutral buildings, leveraging climate-adapted systems and interdisciplinary strategies to reduce investment and operational costs while promoting energy-efficient development.
Surface to Volume Ratio in Buildings
This project analyzes building geometry and façades to optimize renewable energy production, examining how surface-to-volume ratio, shading, orientation, and panel tilt influence heat gain and solar energy capture through conduction, convection, and radiation.