Introduction
As
the
easiest
and
cheapest
way
of
authenticating
an
end
user,
password-based
authentication
methods
have
been
consistently
employed
by
organizations
and
businesses
as
the
default
mechanism
of
restricting
and
monitoring
access.
The
increased
adoption
of
cloud
applications
and
third-party
services
within
an
enterprise
generally
requires
employees
to
keep
track
of
a
number
of
user
names
and
passwords
on
a
daily
basis.
The
fact
that
employees
need
to
remember
multiple
login
credentials
has
incurred
significant
costs
for
an
enterprise
due
to
the
increasing
number
of
help
desk
calls
for
pass-
word
reset.
Moreover,
the
current
practice
of
using
multiple
user
names
and
passwords
in
enterprises
is
also
exposing
the
business
to
more
opportunities
for
security
breaches,
as
demonstrated
by
recent
password
leaks
in
big
brands
such
as
Apple,
Adobe,
and
LinkedIn.
This
project
is
based
on
the
work
on
Loxin
–
A
Solution
to
Password-less
Universal
Login,
published
in
2014
by
Bo
Zhu,
Xinxin
Fan
and
Guang
Gong.
The
core
architecture
and
methodology
of
the
secure
password-less
authentication
system
LOXIN
are
protected
by
U.S.
Patent
10136135
(filed
on
April
15,
2015,
awarded
in
Dec
2018).
Research
topics
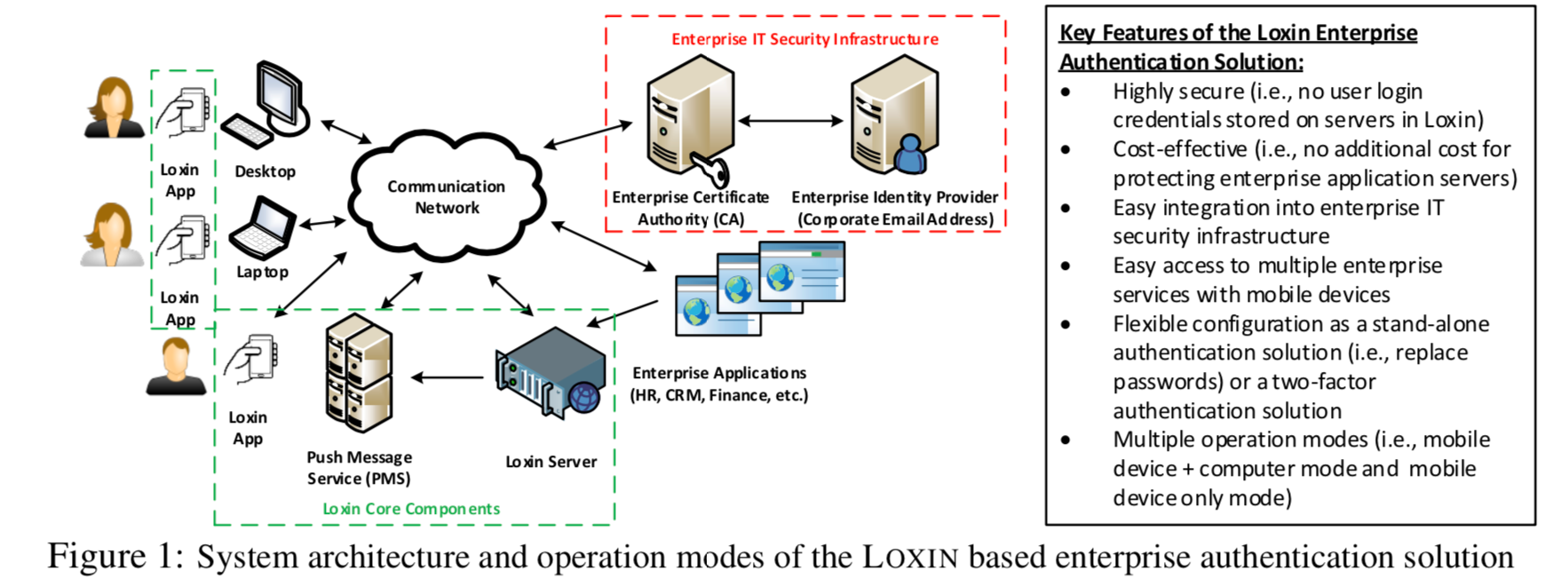
A high-level system architecture and operation modes of LOXIN based enterprise authentication solution are shown in Figure 1.
-
Developing
the
Loxin
mobile
application,
web
APIs
and
the
Loxin
server
software.
Implementation
of
the
core
functionalities,
and
developing
an
app
for
smartphones
and
testing
its
functionality
includes
the
core
functionalities
on
an
Android
emulator:
1)
cryptographic
operations
such
as
generating
public/private
key
pairs,
and
computing
digital
signatures;
2)
connecting
the
enterprise
CA,
the
Loxin
server,
and
the
PMS
via
the
Internet
for
registration,
authentication
and
revocation;
3)
secure
storage
for
the
user's
private
key
in
the
application
(perhaps
in
an
encrypted
format),
and
preventing
unauthorized
accesses
without
proper
(biometric)
authentication.
The
server-side
development
of
web
APIs
and
the
Loxin
server
software
consists
of
two
tasks,
namely
implementing
the
Loxin
Server,
and
developing
a
collection
of
modules
for
application
program
interfaces
(APIs)
and
web
services.
-
Threat
and
risk
assessment
of
the
Loxin
system.
Further
security
analysis
of
the
loxin
system
will
be
conducted
by
considering
deployment
scenarios
and
real-world
threat
models.
We
consider
to
use
some
tools
to
formally
verify
the
correctness
of
the
protocols.
The
attacks,
namely
man-in-the-middle,
mobile
phishing
attacks,
and
other
social
engineering
attacks
such
as
smishing
and
impersonation
attacks
will
be
considered,
especially,
phishing
attacks
which
have
become
more
sophisticated
and
effective.
Threats
and
risks
from
those
attacks
will
be
assessed.
Design
a
penetration
test
for
the
loxin
system
where
the
white-box
testing
approach
will
be
taken,
and
information
such
as
IP
addresses
of
the
servers,
the
Loxin
protocol
details
plus
source
code,
and
the
network
infrastructure
schematics
will
be
exploited
to
conduct
the
test.
References:
B.
Zhu,
X.
Fan,
and
G.
Gong.
“Loxin
–
A
Solution
to
Password-less
Universal
Login".
In
2014
IEEE
Conference
on
Computer
Communications
Workshops
(INFOCOM
WKSHPS),
pages
488–493,
April
2014.