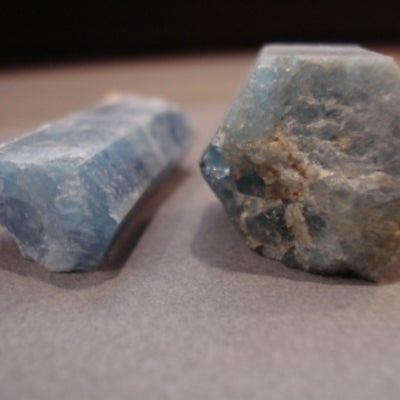
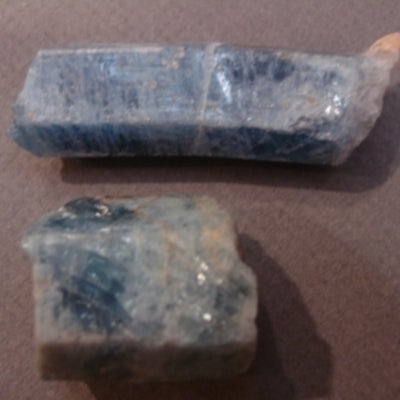
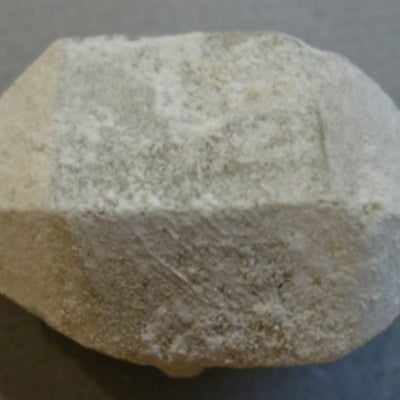
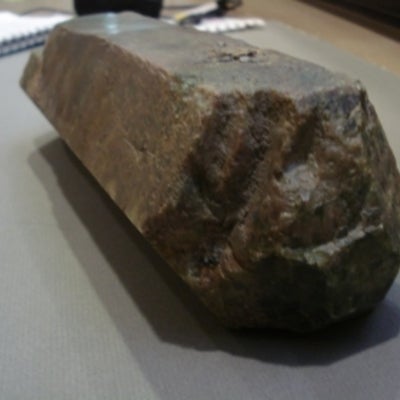
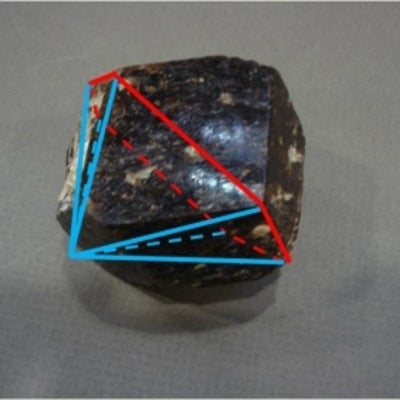
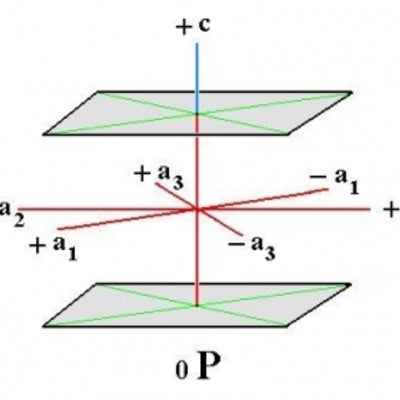
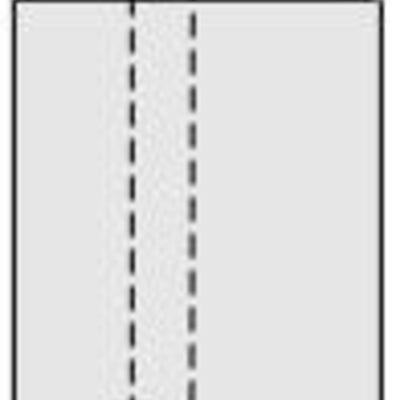
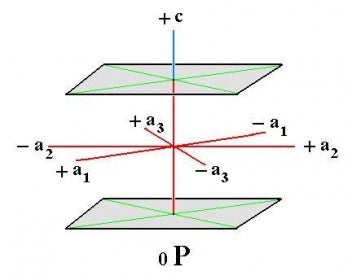
The hexagonal system has four crystallographic axes consisting of three equal horizontal, or equilateral axes at 120 degrees to each other, as well as one vertical axis which is perpendicular to the other three. This vertical axis can be longer or shorter than the horizontal axes.
The system has the following forms:
- Prism
- Pinacoid
- Dipyramid
- Ditrigonal Pyramid
- Trigonal Prism
- Ditrigonal Prism.
1 / 16
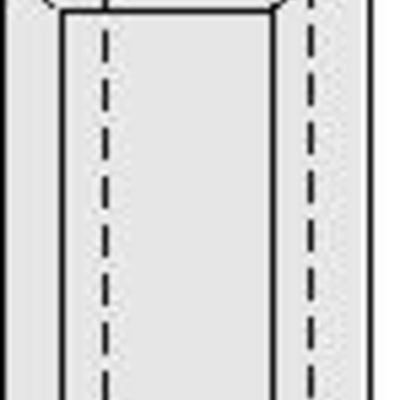
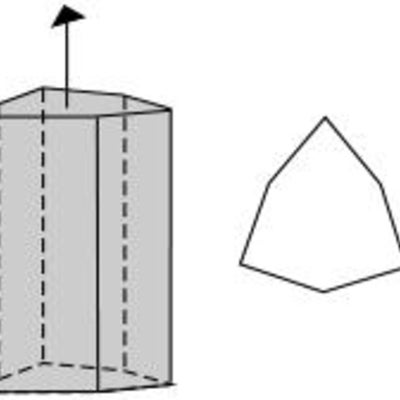
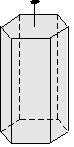
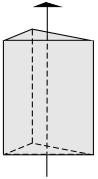
Prisms have a set of faces that run parallel to an axis of a crystal, yet never converge with it. The hexagonal prism is composed of 6 faces which are parallel to a 6-fold rotation axis.
2 / 16
A pinacoid is composed of only two parallel faces. In this case, the top and bottom face are the pinacoid forms.
5 / 16
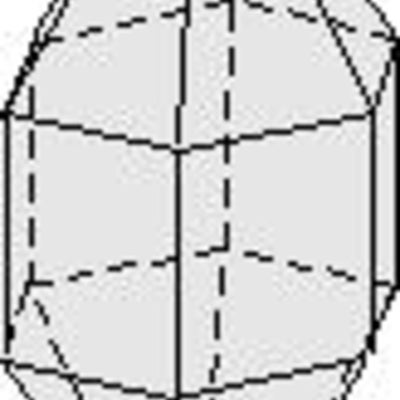
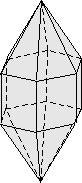
Hexagonal dipyramid: 12-faced form which has a 6-fold axis and comes together in a point. In the image below this would be the top and bottom portion. The vertical faces make up the hexagonal prism, in which all faces in the prism have a 6-fold rotation axis.
10 / 16
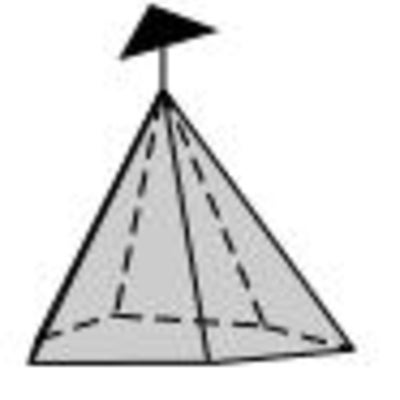
Ditrogonal pyramid: In a ditrigonal pyramid there are six faces about a 3-fold rotation axis. These faces come together and meet in a point.
13 / 16
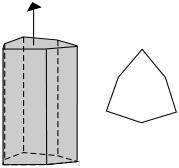
Trigonal prism: A trigonal prism has three faces parallel to each other about a 3-fold rotation axis
14 / 16
Ditrogonal prism: A ditrigonal prism is very similar to the trigonal prism but this form has six faces instead of three. Once again, these faces are parallel about a 3-fold rotation axis.

15 / 16
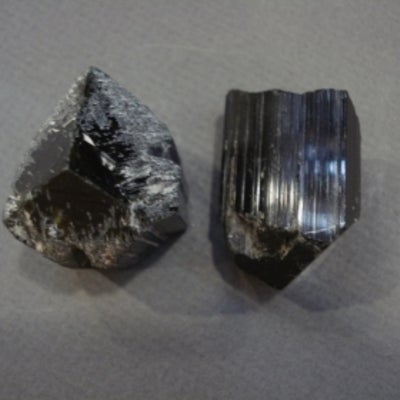
Tourmaline: hexagonal system with two trigonal prisms and trigonal pyramid forms
16 / 16
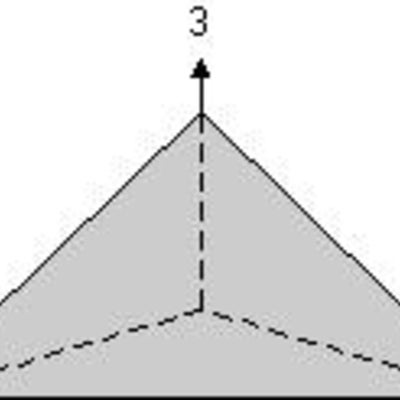
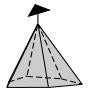
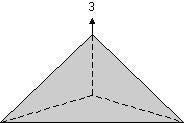
Trigonal pyramid: A trigonal pyramid has three faces about a 3-fold rotation axis which all meet at a point
Diagrams from http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/eens211/forms_zones_habit.htm