Quantum simulators have the potential to bring unprecedented capabilities in areas such as the discovery of new materials and drugs. Engineering precise and programmable interaction graphs between qubits or spins forms the backbone of simulator applications. The trapped ion system is unique in that the interaction graph between qubits can be programmed, in principle arbitrarily. In the context of quantum many-body physics simulation, a programmable interaction graph will allow us to investigate a wide range of spin models relevant to condensed matter systems and high energy physics. In this project we investigate the feasibility of creating an arbitrary qubit-qubit interaction graph and experimentally characterize the interactions. The robustness of such graphs, including errors from experimental parameters, will be analyzed in collaboration with Roger Melko’s group. We will combine theoretical ideas from quantum information processing and many-body physics, numerical optimization and machine learning techniques, and experimental optical and atomic physics techniques. This project will enhance the capability of trapped ion quantum simulators significantly beyond the state-of-the-art and will identify a set of concrete many-body physics problems that can be realistically simulated. Altogether these contributions will form an enabling step towards the scalability of a quantum processor.
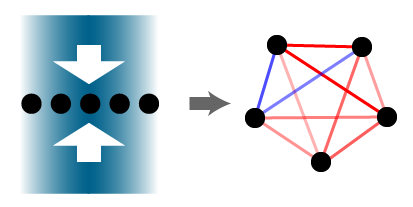
Figure 1. Trapped ion qubits (black discs) are essentially a fully-connected system. The goal of this project is to engineer and characterize the qubit-qubit interaction graph (represented by the red and blue bonds) using precisely tuned laser beams (blue shades with white arrows).