In this project, we build a solid-state quantum simulator for engineering a specific Hamiltonian. Quantum simulators are purpose-built devices with little to no need for error correction, thereby making this type of hardware less demanding than universal quantum computers. Our platform consists of exciton-polariton condensates in multiple quantum-wells sandwiched in a semiconductor Bragg stack onto which a two- dimensional lattice was imprinted. The lattice imprinting can be achieved, for example, by partial etching of the spacer with the lattice pattern followed by an overgrowth of the upper layers of the Bragg structure.
We are particularly interested in exciton-polariton condensates in a kagome lattice, where we can identify topological properties as a function of particle density. A standard optical technique allows us to quantify wavefunctions of exciton-polaritons. To do this, we construct an interferometer for measurement and use power- dependent photoluminescence to identify quantum phases in the kagome lattice.
Our goal is to advance the measurement of topological parameters and knowledge of condensed matter physics in engineered exciton-polariton simulators. This will serve to elucidate quantum phases in a controlled manner and bring us closer to a quantum simulator capable of delivering meaningful insights into quantum materials and optimization.
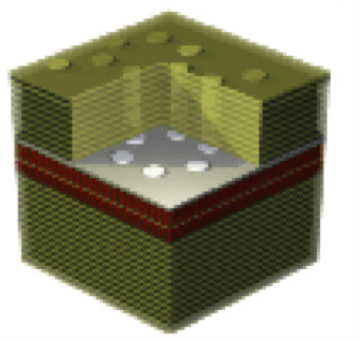
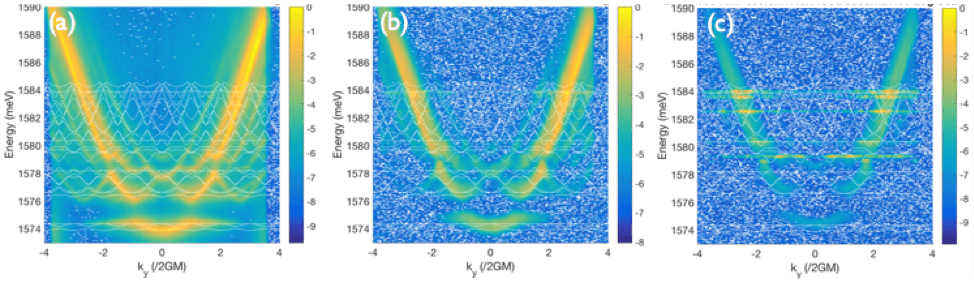
Figure 1. (top) A hexagonal lattice of micro-cavities formed in a Bragg stack structure with a spacer (white layer) sandwiching multiple quantum wells (red layers). (bottom) Bandstructures of exciton-polaritons in a two-dimensional kagome lattice. As the pump power changes, exciton-polaritons undergo phase transition to form coherent states: below threshold (a) P/Pth ~ 0.04, near threshold (b) P/Pth ~ 1, and above threshold (c) P/Pth ~ 2, where Pth is the threshold pump power.