New paper on groundwater contamination by geogenic arsenic
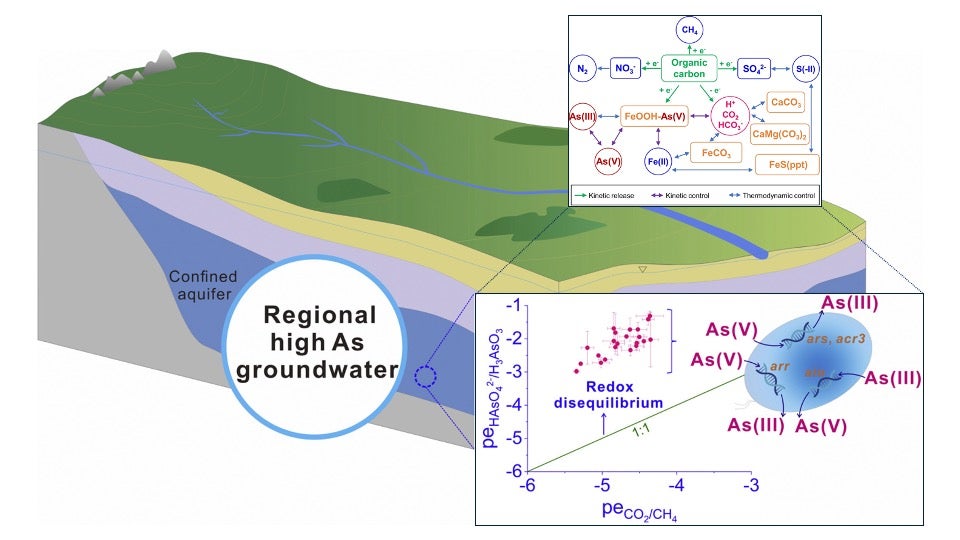
A new paper entitled “Arsenic redox disequilibrium in geogenic contaminated groundwater: Bioenergetic insights from organic molecular characterization and gene-informed modeling” was published in the journal Water Research. The paper presents results from quantitative metagenomic sequencing and ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS) in arsenic (As) contaminated groundwater of the Datong Basin in northern China. The research explores the links between the vertical distributions of As metabolic gene assemblages and that of the Gibbs energy density of dissolved organic matter (DOM). The DOM’s energy content controls the depth interval over which arsenic redox transformations are taking place. In the same depth interval, significant overlap is observed between genes encoding for As reduction and As oxidation. The latter explains why As(V) and As(III) co-exist in the reducing groundwater environment. The paper’s first author is Dr. Kunfu Pi, a former Postdoctoral Fellow in the Ecohydrology Research Group and now a Professor at China University of Geosciences (CUG-Wuhan). Co-authors include Philippe Van Cappellen and colleagues from CUG. To download the paper, visit:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0043135424013587