In this project we develop a quantum interface between microwave and optical photons as a key enabling technology of a hybrid quantum network. In such a network, the robust optical photons carry quantum information through optical fibres over long distances, while superconducting microwave circuits protected from thermal photon noise by the low temperature environment of a dilution refrigerator function as quantum nodes, providing memory, processing and routing capability. Our work includes developing an integrated, microfabricated device that interfaces the fragile microwave photons and with optical photons through either individual or ensembles of three-level solid-state quantum emitters, such as nitrogen vacancy (NV) centers in diamonds. In addition, we are developing novel quantum memory and repeater designs. Here the device itself could serve as an optical quantum memory, storing information in the ground states where we may perform quantum control via a microwave circuit. It could also serve as a specialized quantum node. Entangling operations between remote superconducting circuits can be performed for repeater operation. Finally, we will also develop an efficient microwave photon detector that works by converting microwave photons into optical photons, which can then be efficiently detected with existing technology.
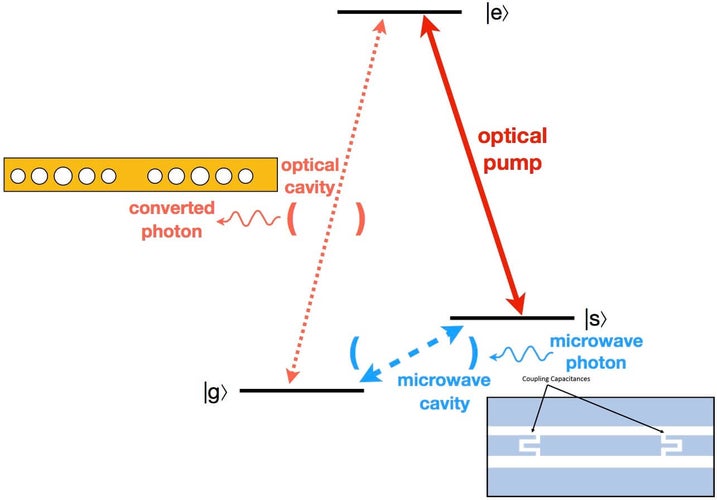
Microwave to optical conversion with a three level quantum emitter coupled to a microwave stripline cavity and an optical, e.g. a photonic crystal, cavity: A microwave photon couples the two ground states |g> and |s> of a three-level quantum emitter with the help of the microwave cavity. The conversion is then completed through an optical pump and an enhanced emission into optical cavity coupled to the transition between the excited state |e> and the ground state |g>.