This project develops new sources of light that utilize quantum entanglement to enhance imaging resolution and detection. We aim to go beyond simple photon pairs and advance our understanding and control of new quantum states of light. Our approach uses deterministic single-photon subtraction (removing of a specific photon from a pulse of light) implemented with three-level solid-state quantum emitters, such as quantum dots and colour centers in diamond, coupled to chiral waveguides. In this type of waveguide, light propagation direction is determined by light’s polarization. Our goal is to cascade multiple photon subtraction stages on a chip-scale device and explore deterministic photon subtraction as a tool for engineering quantum states of light for improved resolution of optical microscopy and long range optical sensing.
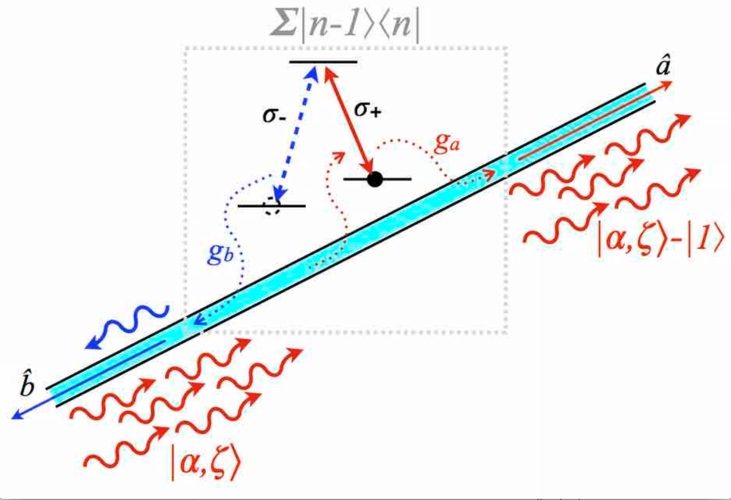
Figure 1. A three-level quantum emitter with circularly polarized transitions between its ground and excited states is strongly coupled to a chiral waveguide to form a device that can deterministically subtract single photon from input light. This can be used to generate highly non-classical states from, e.g., squeezed coherent states.