Screening for COVID-19 with AI
Open-source project takes next step with release of new models, largest datasets of CT scans

Open-source project takes next step with release of new models, largest datasets of CT scans
By Brian Caldwell Faculty of EngineeringResearchers at Waterloo Engineering have taken another step forward in their open-source COVID-19 project with the release of new datasets and artificial intelligence (AI) models that were built using them.
Launched in March, the initiative involves the use of deep-learning AI software to screen chest x-rays and CT scans for evidence of infection and degree of disease progression.
The new datasets, released as part of the COVID-Net project, include CT scans from over 4,500 patients in more than 15 countries, making them the largest and most diverse resources of their kind in the world.
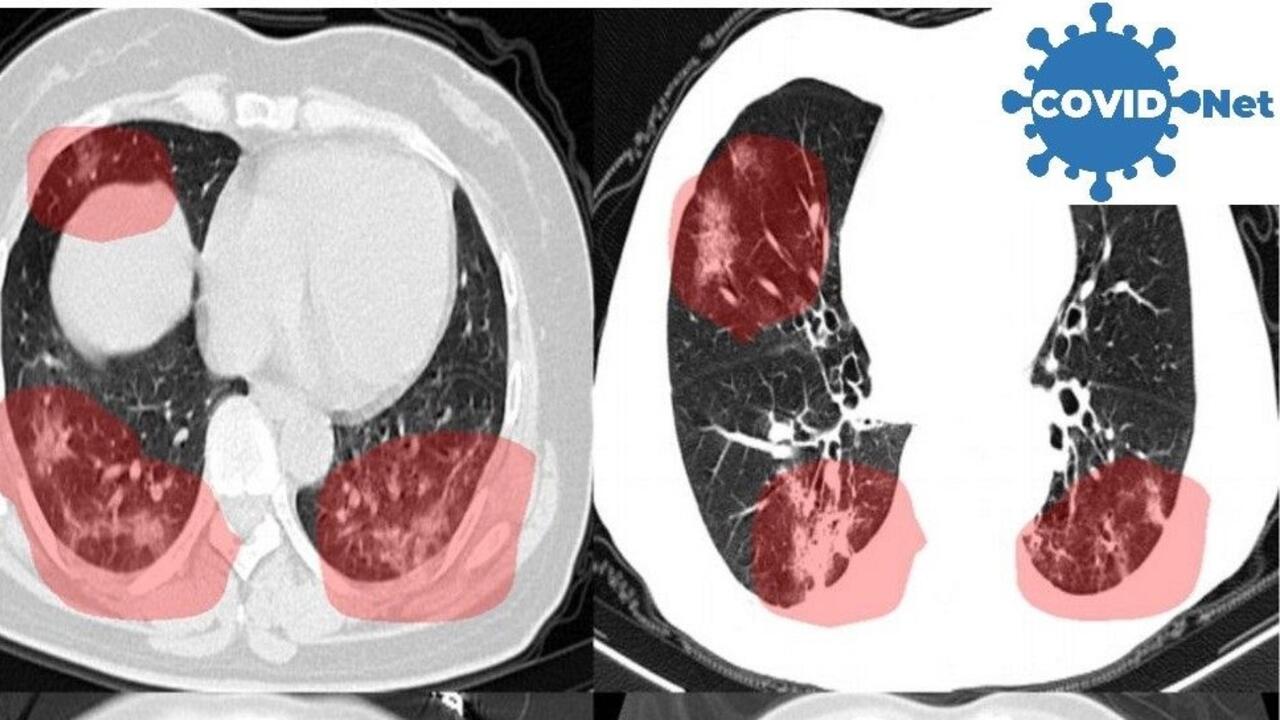
The new AI models, dubbed COVID-Net CT-2, have been found via explainable AI to make their decisions on COVID-19 screening with CT scans using some of the same types of visual cues as expert radiologists.
“Taking this path enables building AI with much greater transparency and trust,” Alexander Wong, a professor of systems design engineering, Canada Research Chair in Artificial Intelligence and Medical Imaging, and a director of the Vision and Image Processing (VIP) Research Group, wrote in a post announcing the new developments.
“We hope making the AI models and datasets available will drive global innovation in healthcare.”
Photo: CT scans of lungs show areas of concern highlighted in red by new AI models developed by Waterloo Engineering researchers.
Read more
Two University of Waterloo affiliated health-tech companies secure major provincial investment to bring lifesaving innovations to market

Read more
Researchers engineer bacteria capable of consuming tumours from the inside out

Hand holding small pieces of cut colourful plastic bottles, which Waterloo researchers are now able to convert into high-value products using sunlight. (RecycleMan/Getty Images)
Read more
Sunlight-powered process converts plastic waste into a valuable chemical without added emissions
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.