
Social norms strongly influence vaccination decisions and the spread of disease
Societal pressures about vaccination have a direct effect on the spread of pediatric infectious diseases in areas where inoculation is not mandatory.

Societal pressures about vaccination have a direct effect on the spread of pediatric infectious diseases in areas where inoculation is not mandatory.
By Media RelationsOur response to societal pressures about vaccination has a direct effect on the spread of pediatric infectious diseases in areas where inoculation is not mandatory, says new research published this week in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
By incorporating social norms into predictive mathematical modelling, a research team from the University of Guelph and the University of Waterloo found that they can foresee the observed patterns of population behaviour and disease spread during vaccine scares—times when anti-vaccine sentiment is strong.
"If vaccination is not mandatory and disease is rare, then a few parents will be tempted to stop vaccinating their children," said Professor Chris Bauch of Waterloo's Faculty of Mathematics, and one of the study authors. "More parents adopt this behaviour as social norms begin to change and it becomes increasingly acceptable to avoid some vaccines. Obviously, when enough parents are no longer vaccinating, the disease will come back."
In most of North America, pediatric vaccination is mandatory for children enrolled in public education. However, the number of parents applying for exemptions to pediatric vaccination is on the rise. According to Professor Bauch, as that trend continues Canadians will increasingly find themselves in a situation where vaccination coverage has declined and populations are once again susceptible to disease.
"Parents are not cold, clinical rationalists who base their decisions only on data. They are strongly influenced by other parents and what they read," said Professor Bauch. "Our research suggests that health officials needs to have a really good understanding of the social context to better understand vaccine scares and why people refuse vaccines. To do that, we have to develop predictive tools that also reflect social behavior patterns, or we won’t be able to accurately represent what is happening during vaccine scares."
Predictive modelling can help public health officials plan for responses to vaccine programs. The models that Professor Bauch and his colleagues use can determine what may happen in a population where a vaccine scare has taken hold.
"If you’ve seen a big drop in vaccine coverage and you’ve seen a surge of disease because of that, you can use these models to predict how long it will take vaccine coverage to recover," said Professor Bauch.
Professor Bauch and his colleagues will continue to study how social norms interact with disease spread. Down the road, he hopes to use this model to create an index, which may be able to help determine which populations are more susceptible to vaccine scares, with the hope of preventing them from occurring.
In just half a century, the University of Waterloo, located at the heart of Canada's technology hub, has become one of Canada's leading comprehensive universities with 35,000 full- and part-time students in undergraduate and graduate programs. Waterloo, as home to the world's largest post-secondary co-operative education program, embraces its connections to the world and encourages enterprising partnerships in learning, research and discovery. In the next decade, the university is committed to building a better future for Canada and the world by championing innovation and collaboration to create solutions relevant to the needs of today and tomorrow. For more information about Waterloo, please visit www.uwaterloo.ca.
-30-
Pamela Smyth
University of Waterloo
519-888-4777
www.uwaterloo.ca/news
@uWaterlooNews
Attention broadcasters: Waterloo has facilities to provide broadcast quality audio and video feeds with a double-ender studio. Please contact us to book.

Read more
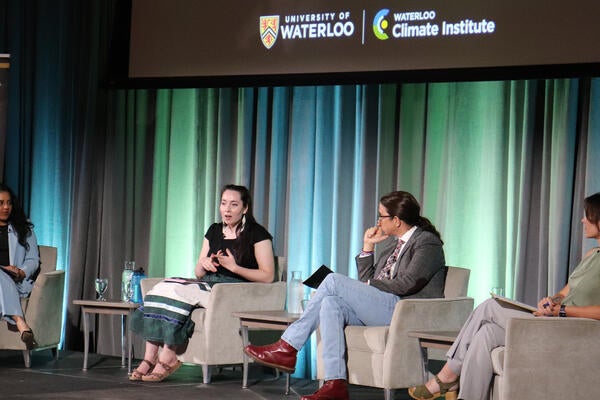
TRuST Scholarly Network hosts conversation on charting a course through climate misinformation to promote informed climate action

Read more
Brian Orend brings a philosopher’s perspective on happiness, navigating the challenges of chronic illness through connection to ourselves and others
Read more
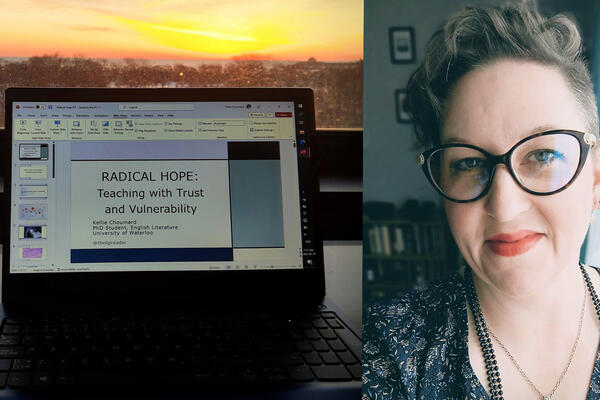
After a breast cancer diagnosis during the pandemic, Kellie Chouinard turned to social media for support. Learn how this experience shaped her groundbreaking research.
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.