Tackling the coronavirus pandemic
Waterloo Engineering researchers launch global initiative to improve COVID-19 screening using AI software and chest x-rays

Waterloo Engineering researchers launch global initiative to improve COVID-19 screening using AI software and chest x-rays
By Brian Caldwell Faculty of EngineeringResearchers at Waterloo Engineering partnered with an artificial intelligence (AI) startup this week on a project to improve COVID-19 screening.
The research team publicly released AI software that can better detect infections from chest x-rays and is looking to enlist expertise from around the world to aid in the project.
“This software has had promising initial results,” says Alexander Wong, a systems design engineering professor and director of the Vision and Image Processing (VIP) Lab at the University of Waterloo. "We hope that by making this software open, we can attract clinicians and scientists far and wide to improve upon the technology."

Alexander Wong is a systems design engineering professor.
Wong launched the COVID-Net project in conjunction with Waterloo startup DarwinAI, a company he co-founded.
The alternate, AI-assisted, x-ray screening method is meant to augment the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) swab tests now in short supply in many areas of the world on the front lines of the coronavirus pandemic.
“Chest radiography can be conducted quickly and is relatively low-cost and widely available,” Wong says. “It is already used by several countries to complement PCR tests. Augmenting it with AI to improve screening accuracy could have a lot of value.”
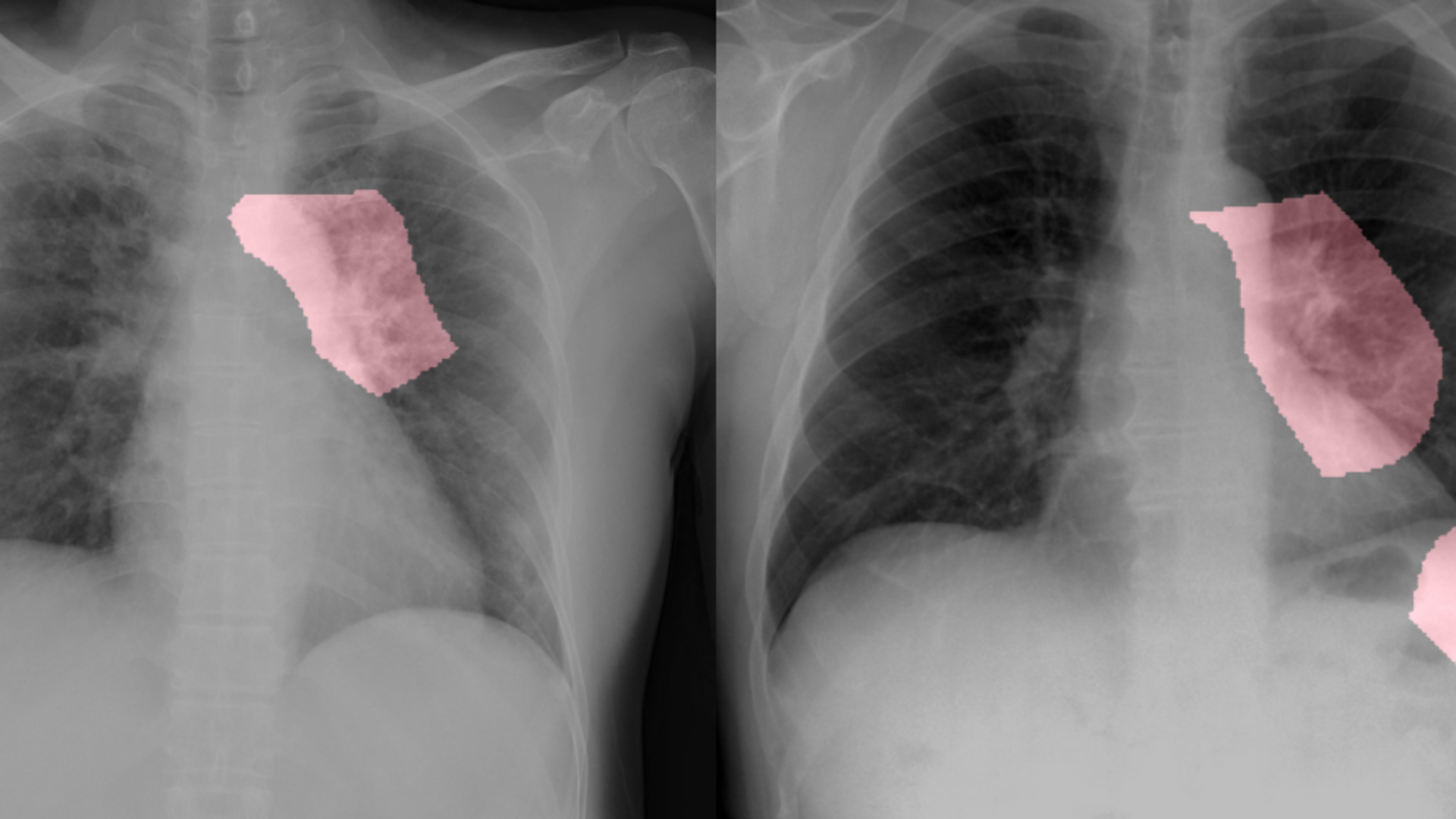
Key areas are highlighted in pink in these chest radiology images of two patients with COVID-19
In addition to the deep-learning AI software researchers developed to detect COVID-19 from chest x-ray images, they have made a dataset and a scientific paper on their work publicly available on GitHub at https://github.com/lindawangg/COVID-Net
"Our hope is that COVID-Net will be used and built upon by clinicians, researchers, and citizen data scientists," says Wong, also a founding member of the Waterloo Artificial Intelligence Institute (Waterloo.ai). "Ideally, this tool will allow us to accelerate the global use and development of effective, radiography-based COVID-19 screening solutions and treatment of those who need it the most."
To develop their screening tool, the researchers used public sources to compile a dataset of almost 6,000 chest radiography images from nearly 3,000 patients.
Sheldon Fernandez, a Waterloo Engineering alumnus and CEO of DarwinAI, says the open-source initiative comes after "grappling with how to best deploy our skills in service of the present crisis."
In order to increase confidence in the new technology, researchers are also making available an explainability tool that shows how their AI technology reaches its COVID-19 detection decisions.
Wong said the explainability tool should build trust in the system and could uncover new insights into visual indicators associated with COVID-19 infections.
Read more
Two University of Waterloo affiliated health-tech companies secure major provincial investment to bring lifesaving innovations to market

Read more
Researchers engineer bacteria capable of consuming tumours from the inside out

Hand holding small pieces of cut colourful plastic bottles, which Waterloo researchers are now able to convert into high-value products using sunlight. (RecycleMan/Getty Images)
Read more
Sunlight-powered process converts plastic waste into a valuable chemical without added emissions
Read
Engineering stories
Visit
Waterloo Engineering home
Contact
Waterloo Engineering
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.