As the demand for digital services grows, so does the need for data centres and transmission networks. Unfortunately, these data systems consume vast amounts of energy, resulting in nearly 1% of all energy-related greenhouse gas emissions. This project aims to invent novel quantum devices for highly energy-efficient computing that may help reduce the global digital carbon footprint.
Projects - search
Filter by:
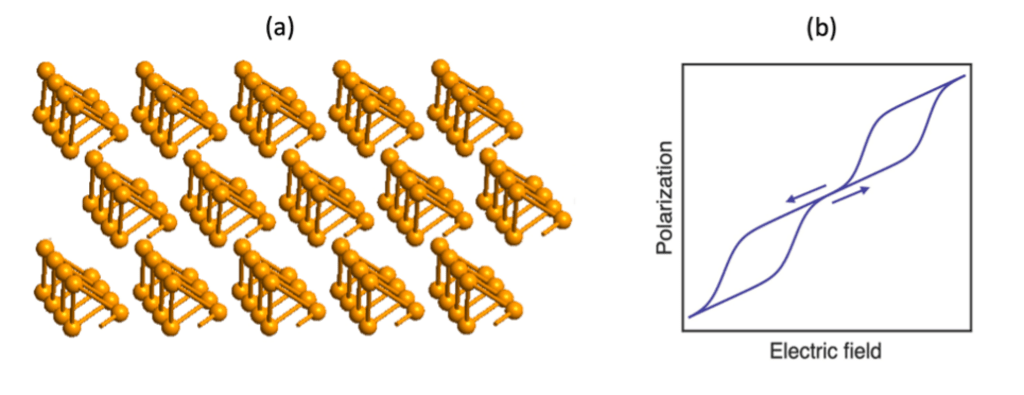
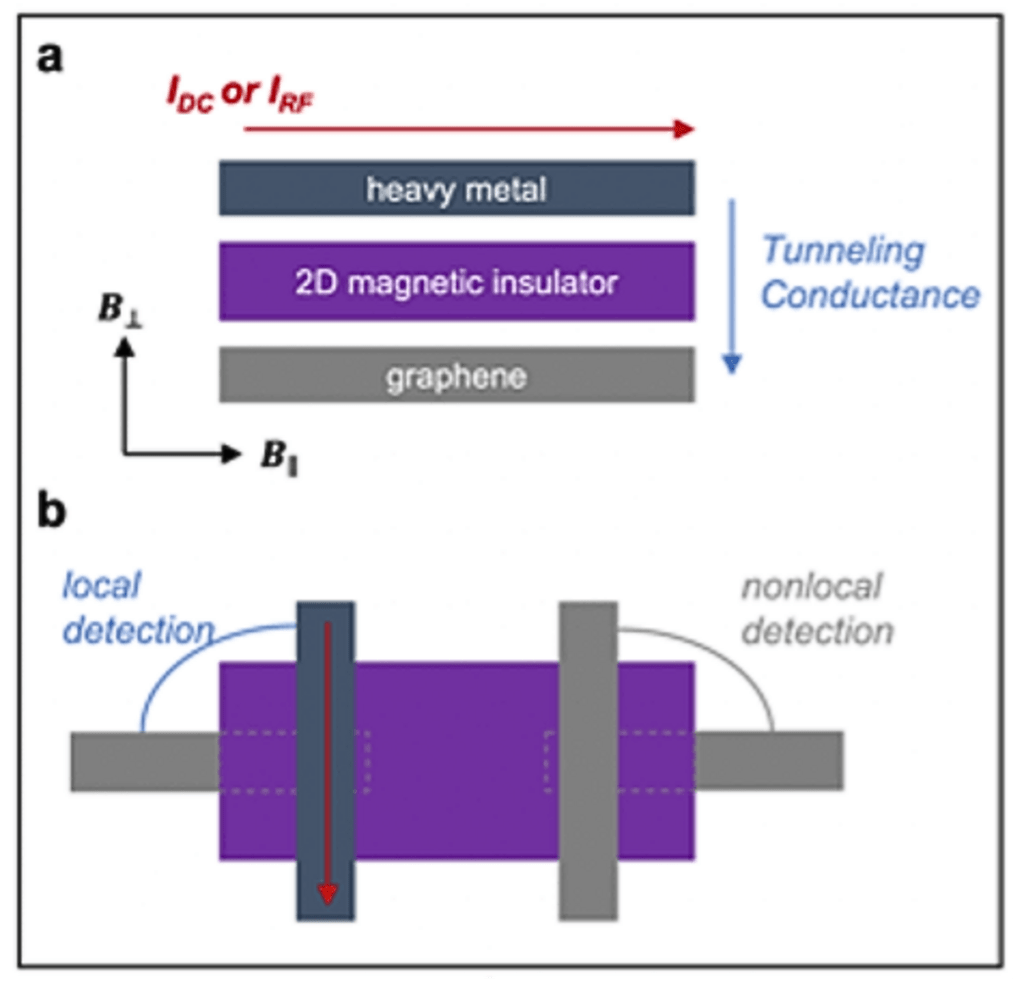
The goals of this project are (1) to generate and detect coherent magnons in 2D magnets for quantum magnonics; and (2) to induce collective quantum states in 2D magnets (magnon BECs and Kitaev QSLs), which can provide an alternative route to defeat quantum decoherence. 2D magnetic insulators interfaced with topological semimetals will be fabricated to generate and detect coherent magnons, magnon BECs and QSLs.
This research aims to achieve experimental realization of superconducting quantum memelements, which has never been done before. A quantum memcapacitor will be fabricated by depositing and patterning thin aluminum films, and then cooling to cryogenic temperatures to unveil quantum-mechanical properties in highly nonlinear regimes.
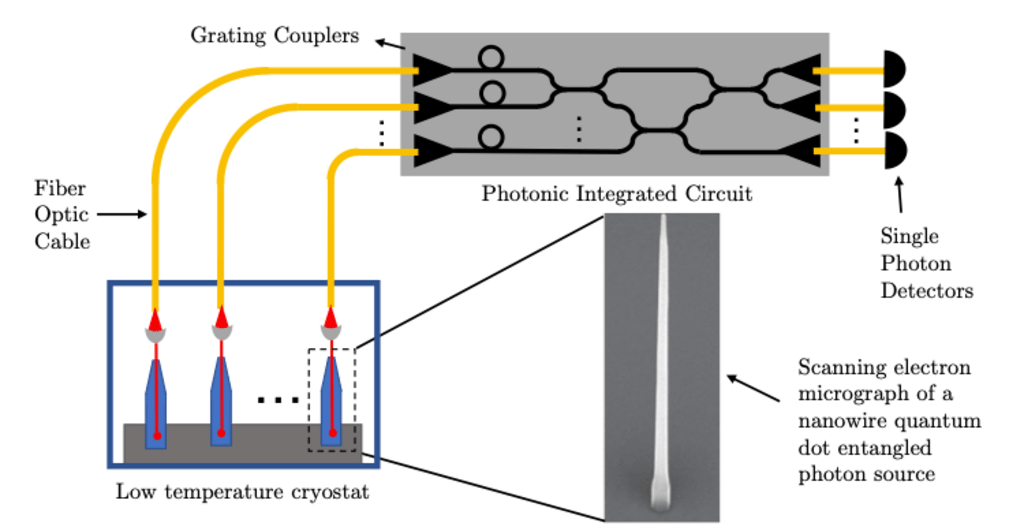
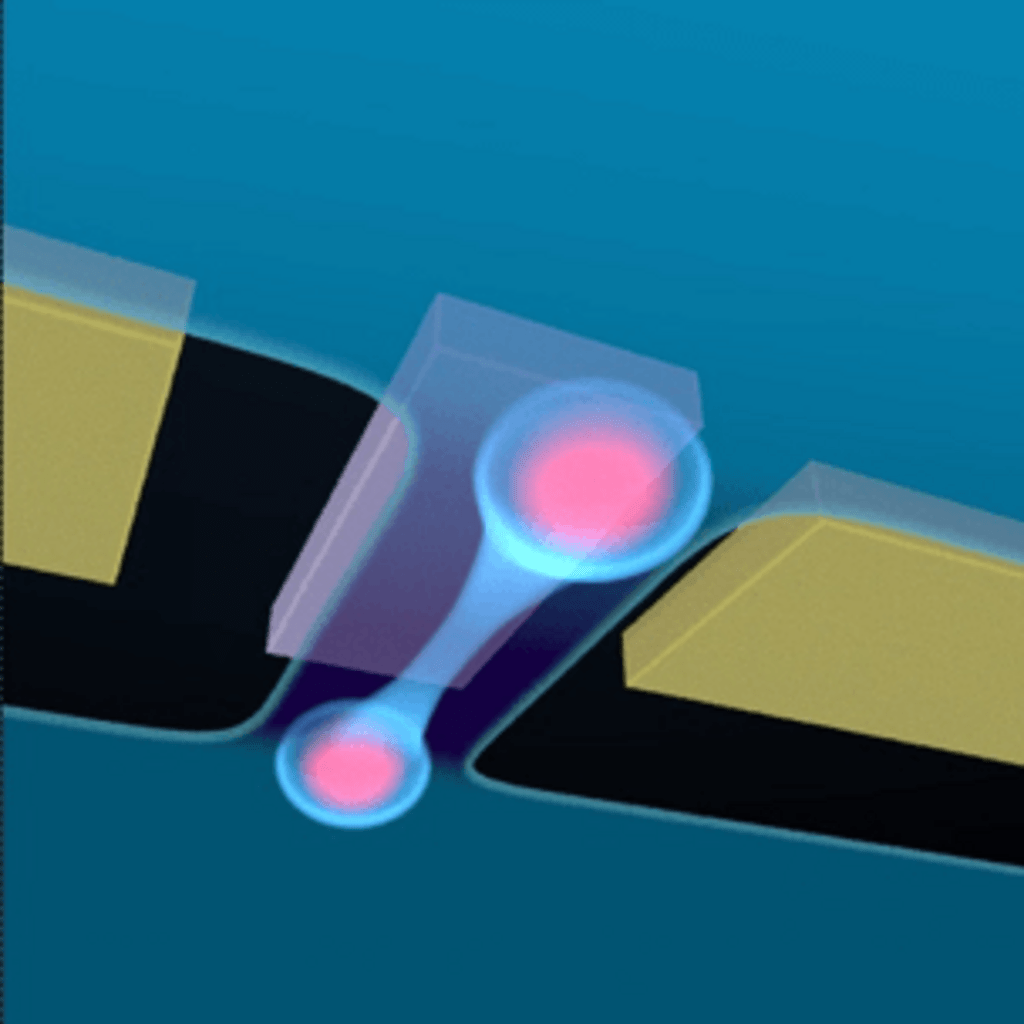
This project aims to boost the speed of on-chip quantum operations by using bright, on-demand entangled photon sources with an extraction efficiency of more than two orders of magnitude higher than the existing state-of-the-art technology based on probabilistic photon sources.
Strongly-coupled field theories describe both fundamental and applied quantum problems. With the goal of exploring these theories, we are working to develop functional quantum simulators, which take advantage of the phenomenon of superposition.
This project aims to provide a suitable material platform to realize MZMs. To achieve this, we develop a high-mobility semiconductor layer structure in order to observe the experimental signature of Majorana fermions on a platform that can be readily scaled and advanced to logical qubit devices.
In this project we seek to improve the capabilities of trapped ion quantum processors, implementing all of the basic tools required to perform quantum information processing with multi-level qudits.
In this project, we develop new theoretical tools for quantum simulations of non-Abelian problems in high energy physics (HEP), and HEP problems beyond one dimension. Our work is conducted in close collaboration with experimental groups to design robust and feasible simulation schemes that are custom-designed to particular quantum platforms.
Our strategy for generating Majorana fermions is to combine helical surface states of topological insulators with superconductors. Through combined electrical and magnetic gating, we are working toward a long-term capability to create and manipulate Majorana fermions over a scalable network.
In this project we synthesize high quality topological insulators and superconductors, couple them together to form a clean interface (“strong proximity”), and use tunneling spectroscopy to identify the presence of Majorana fermions. Once we are able to move the Majorana particles in a controlled fashion, we then braid an array of them and extract topological quantum information. This will provide the first demonstration of non-Abelian statistics on topological insulators and the first realization of topological quantum computing.
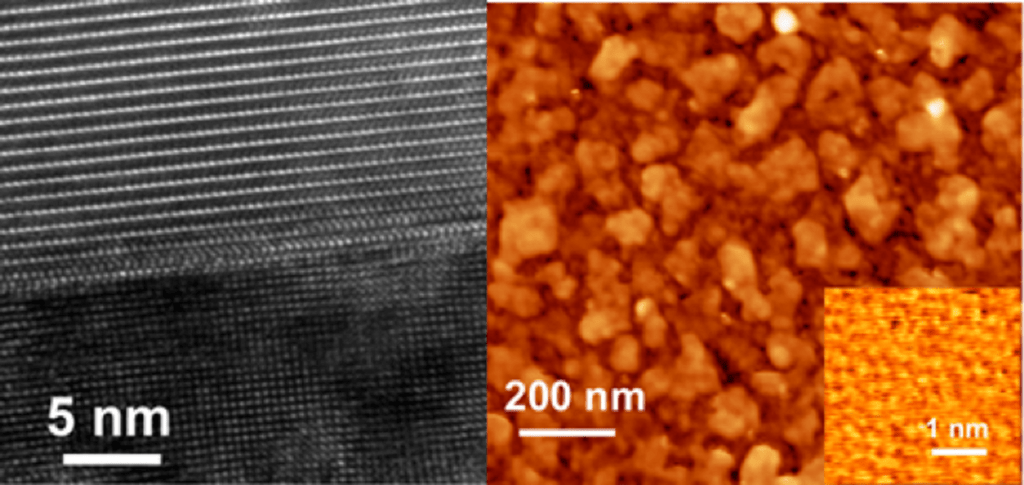
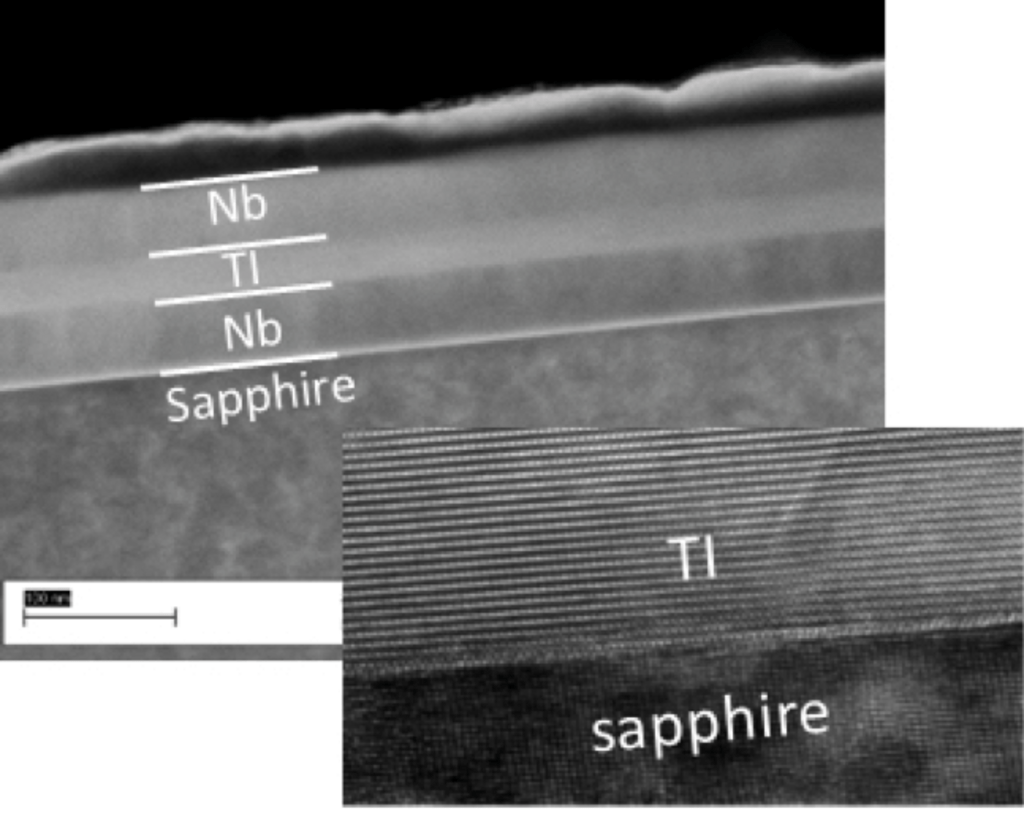
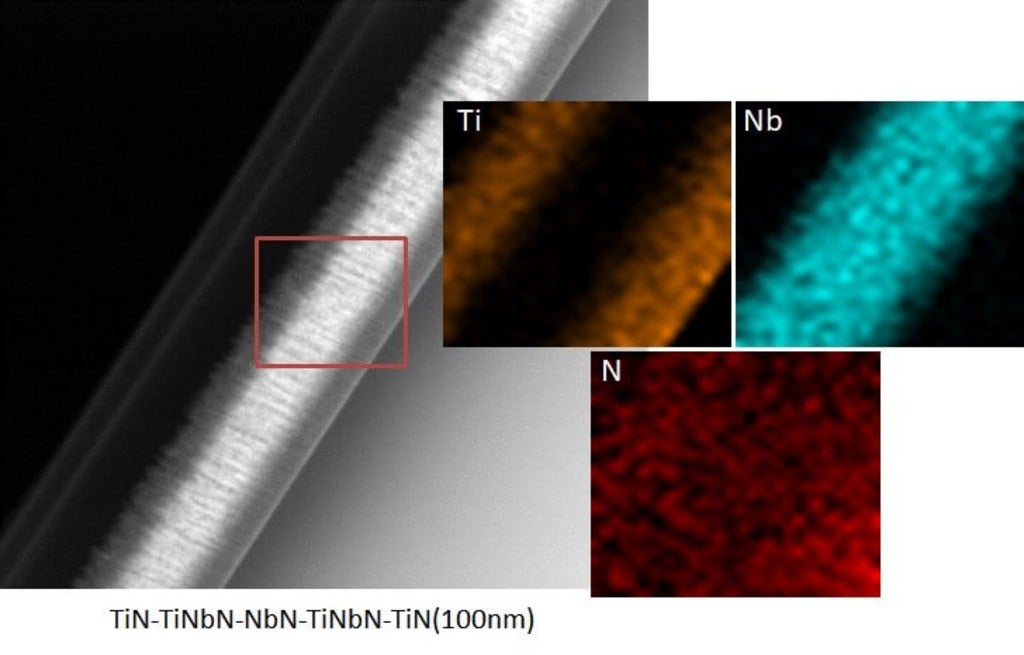
In this project, we will construct composite heterostructures with nitrides, oxides and hybrid materials involving high-temperature superconducting oxides and “conventional” transition metals/nitrides.
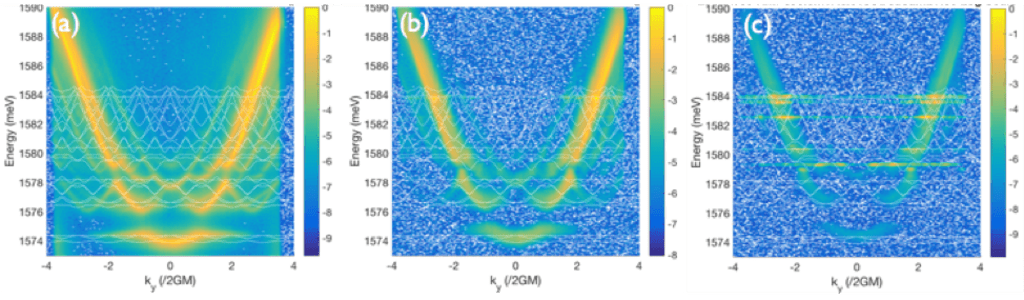
In this project, we build a solid-state quantum simulator for engineering a specific Hamiltonian. Quantum simulators are purpose-built devices with little to no need for error correction, thereby making this type of hardware less demanding than universal quantum computers. Our platform consists of exciton-polariton condensates in multiple quantum-wells sandwiched in a semiconductor Bragg stack onto which a two- dimensional lattice was imprinted. The lattice imprinting can be achieved, for example, by partial etching of the spacer with the lattice pattern followed by an overgrowth of the upper layers of the Bragg structure.
In this project we construct a shared trapped-ion quantum computing platform, QuantumIon, that will enable a broader and interdisciplinary scientific community to access an advanced quantum computing platform, thereby accelerating the discovery of new methods and applications of quantum computing.
This project will enhance the capability of trapped ion quantum simulators significantly beyond the state-of-the-art and will identify a set of concrete many-body physics problems that can be realistically simulated. Altogether these contributions will form an enabling step towards the scalability of a quantum processor.
We are building technologies for the control and measurement of superconducting qubits to enable the first demonstration of an extensible, medium-scale quantum processor.
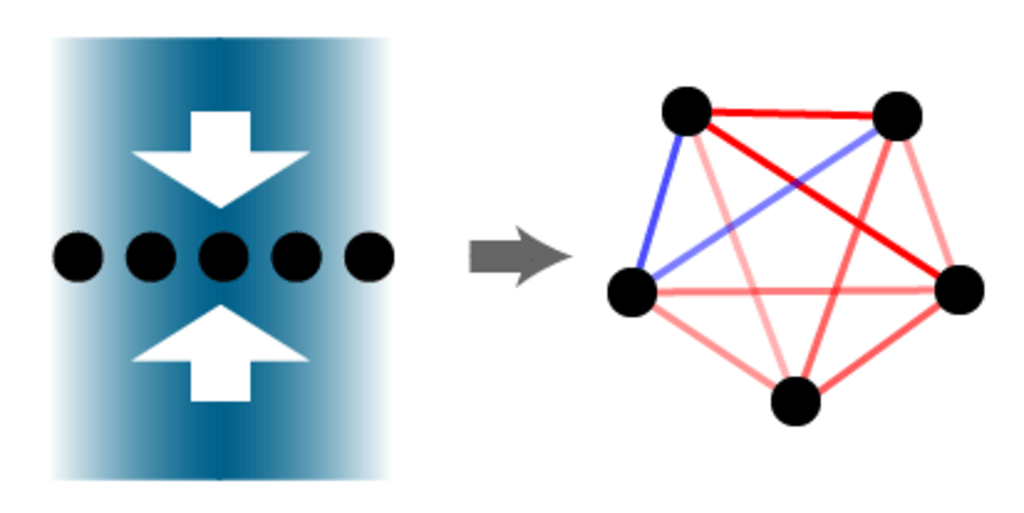
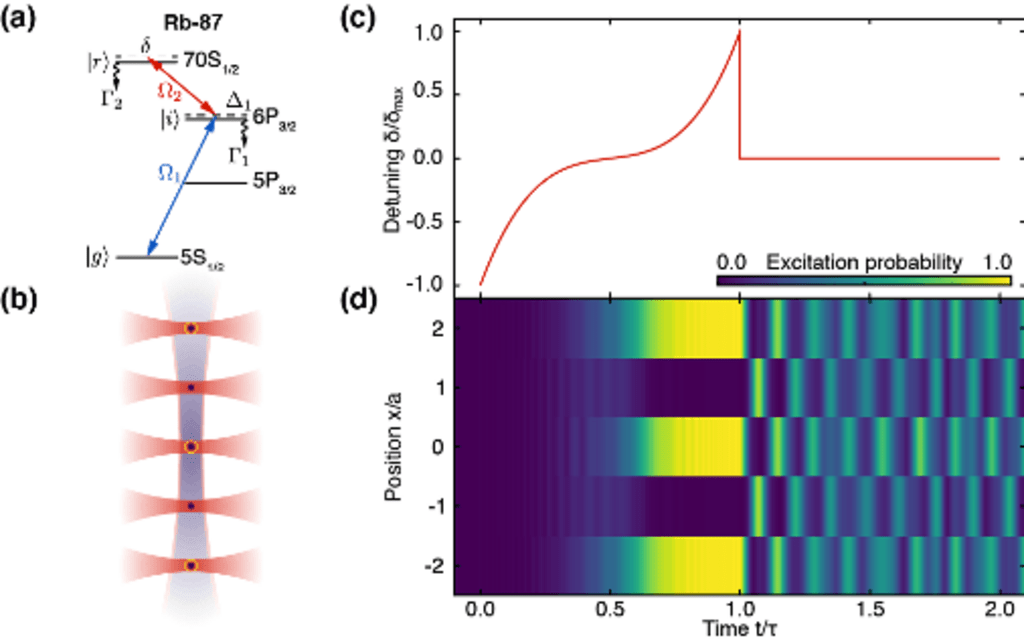
We are developing quantum simulators based on arrays of neutral atoms excited to Rydberg states. Such Rydberg atom arrays are advantageous for simulating the dynamics of interacting spin systems (Ising spin models) in higher dimensions and arbitrary geometries.
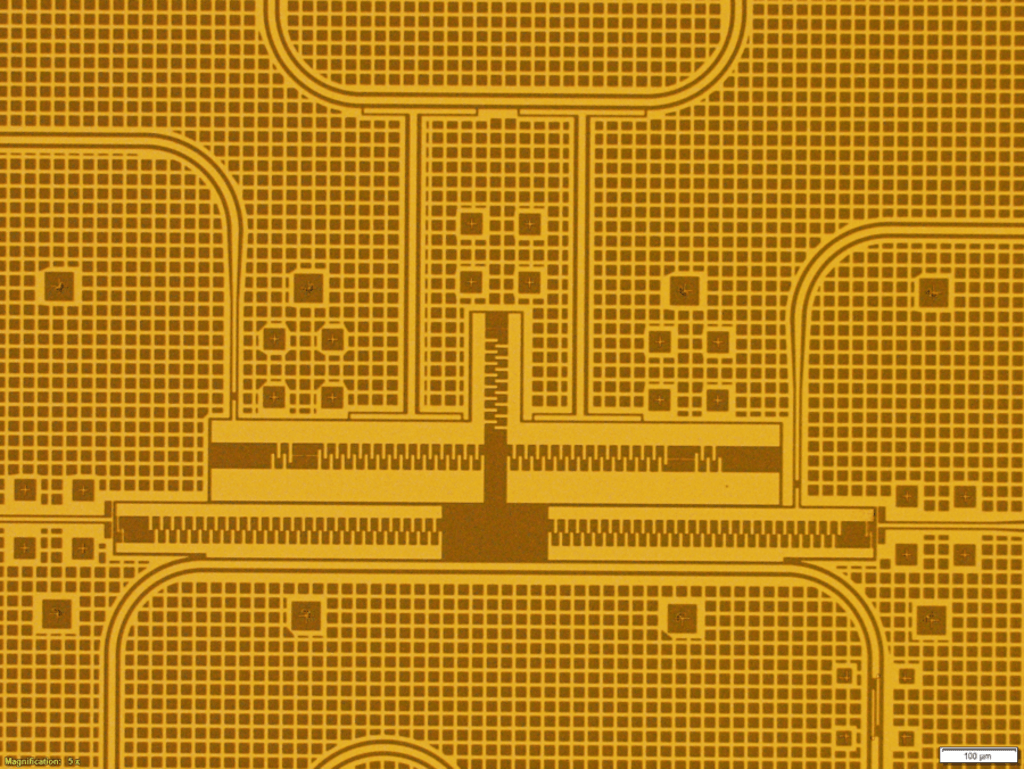
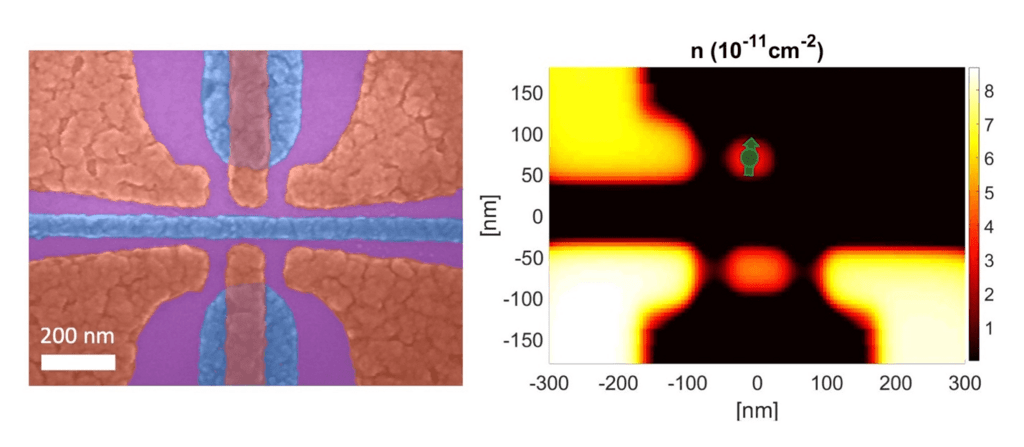
A major focus of this project is to simplify QMOS devices – reducing the number of gate electrodes per device, even down to a single electrode. The team led by Dr. Baugh with collaborators Dr. Lan Wei and Dr. Michel Pioro-Ladrière combines expertise in electrical engineering and CMOS integrated design, QMOS fabrication and physics. By testing the viability of a network/node approach, this project charts a path toward a large-scale quantum information processor in silicon.
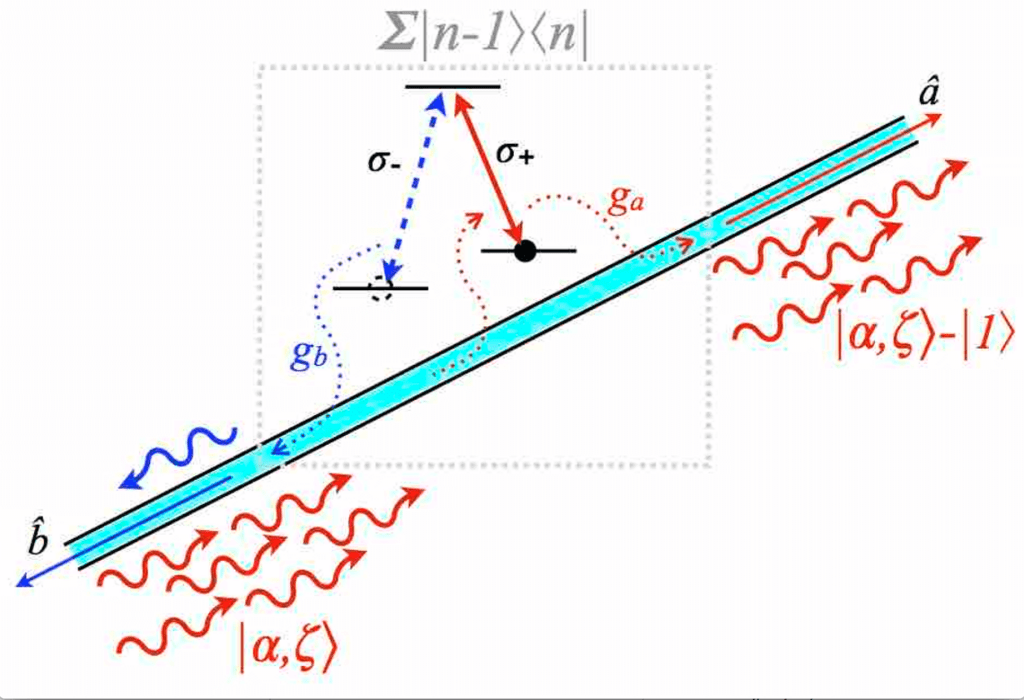
This project develops new sources of light that utilize quantum entanglement to enhance imaging resolution and detection. We aim to go beyond simple photon pairs and advance our understanding and control of new quantum states of light.