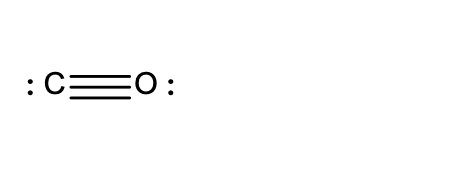UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
19 MAY 2011
TIME: 75 MINUTES
This exam is being written by several thousand students. Please be sure that you follow the instructions below.
We'll send your teacher a report on your performance. Top performers are eligible for a prize. The names of the top 200 students will be published in the September issue of Chem 13 News.
- Print your name here: _________________________
- Print your school name and city on your STUDENT RESPONSE sheet.
- Select, and enter on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet, one of the following CODE numbers:
- Code 1 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a nonsemestered school
- Code 2 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a semestered school
- Code 3 Ontario, Grade 12 Chemistry already completed
- Code 4 Any other Ontario student
- Code 5 Manitoba or Saskatchewan high school student
- Code 6 Québec high school student
- Code 7 Québec CEGEP student
- Code 8 Alberta or British Columbia high school student
- Code 9 New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, or Prince Edward Island high school student
- Code 10 Northwest Territories, Nunavut, or Yukon high school student
- Code 11 High school student outside Canada
- Code 12 Teacher
- Print your name (last name, first name and optional middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed name.
- Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet.
- Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number.
- Mark only one answer for each question.
- Questions are all of the same value.
- There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer.
- Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval.
Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the sheet white again.
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
1. Iodine-131 is a radioactive isotope used to treat hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland) and thyroid cancer.
How many protons, neutrons and electrons are there in a single atom of iodine-131?
- 131 protons, 131 neutrons, 131 electrons
- 53 protons, 78 neutrons, 53 electrons
- 78 protons, 53 neutrons, 78 electrons
- 53 protons, 131 neutrons, 53 electrons
- 78 protons, 131 neutrons, 78 electrons
2. Data are given below for the hypothetical element avogadrium, symbol Av.
What is the average atomic weight of avogadrium?
| Isotope | Relative weight | Fractional abundance |
|---|---|---|
| Av-58 | 58.017 u | 36.02% |
| Av-60 | 60.154 u | 63.98% |
- 58.79 u
- 59.09 u
- 58.55 u
- 59.38 u
- 59.62 u
3. Which of the following equations is not correct?
- H₂(g) → 2 H(g) + energy
- Na(g) + e⁻ → Na⁻(g) + energy
- Mg(g) + energy → Mg²⁺(g) + 2e⁻
- Cu(s) + energy → Cu(l)
- Na⁺(g) + Cl⁻(g) → NaCl(s) + energy
4. How many electron pairs are there around the S atom in the SF₄⁻ ion?
- three bonding pairs
- three bonding pairs and one unshared pair
- three bonding pairs and two unshared pairs
- four bonding pairs and two unshared pairs
- six bonding pairs
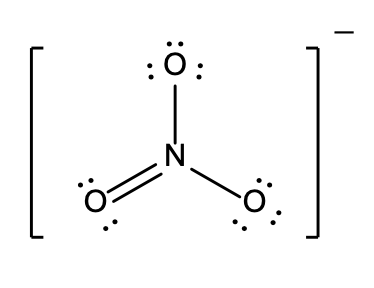
5. A student prepared the following graph to illustrate one aspect of ideal gas behaviour.
However, he forgot to label the axes.
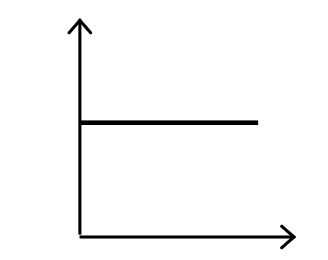
Note: In the responses below, the symbols have their usual meanings: P is pressure; V is volume, T is kelvin temperature; n is amount in moles.
- P versus T, with n and V held constant
- T versus n, with P and V held constant
- PV versus T, with n held constant
- P versus V, with n and T held constant
- PV/T versus P, with n held constant
6. Which substance, in the solid state, is likely to have the following characteristics: hard; brittle; soluble in water; high melting point?
- Cl₂
- RbCl
- C(diamond)
- Cu
- IBr
7. The mass of a sample is measured as 0.03050 g.
How many significant figures are there in this quantity?
- two
- three
- four
- five
- six
8. Graphite is best described as
- a hard, white solid
- a soft, white solid
- a soft, black solid
- a hard, silvery solid
- a yellowish liquid
9. According to the World Health Organization, the development of methods for the disinfection of drinking water is considered one of the major achievements of modern times.
Which of the following substances has been widely used to disinfect drinking water?
- NaF
- O2
- Cl2
- CO2
- HCl
10. By the addition of water, 40.0 mL of 8.0 mol/L HI is diluted to 160.0 mL.
What is the molar concentration of HI after dilution?
- 0.50 mol/L
- 1.0 mol/L
- 1.6 mol/L
- 2.0 mol/L
- 4.0 mol/L
11. Which of the following substances does not produce ions when it is added to water?
- sodium metal, Na
- ethanol, CH3CH2OH
- citric acid, C6H8O7
- carbon dioxide, CO2
- potassium nitrate, KNO3
12. How many grams of B2H6 can be made starting with 5.00 g LiAlH4 and excess BF3 according to the following reaction?
3 LiAlH4 + 4 BF3 → 3 LiF + 3 AlF3 + 2 B2H6
- 1.85 g
- 2.43 g
- 3.65 g
- 5.47 g
- 7.29 g
13. An isotope of a particular element has a mass number of 208 and it has 46 more neutrons than protons.
What is the element?
- mercury, Hg
- polonium, Po
- lead, Pb
- bismuth, Bi
- thallium, Tl
14. The covalent radius of hydrogen is 74 pm.
Assume that hydrogen atoms could be arranged side-by-side in a single line, as suggested in the diagram below.
What is the mass of a line of hydrogen atoms that is exactly 10 cm long?
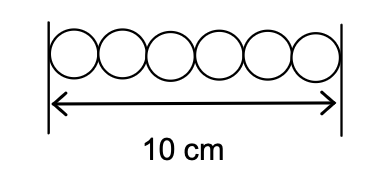
- 7.3×10-10 g
- 1.1×10-15 g
- 2.3×10-15 g
- 1.2×10-21 g
- 7.4×10-11 g
15. What is the H-C-H angle in the ethene molecule, C2H4?
Choose the closest value.
- 45°
- 90°
- 109°
- 120°
- 180°
16. A process for producing iron, Fe, is based on the following reactions.
2 CO(g) + O2(g) → 2 CO(g)
Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g)
What mass of O2 is required to produce 1.0×102 kg Fe?
- 19 kg
- 43 kg
- 50 kg
- 75 kg
- 170 kg
17. To which one of these pairs of elements does the term metalloids apply most fittingly apply?
- potassium and strontium
- nickel and silver
- lithium and beryllium
- sulfur and bromine
- boron and silicon
18. Which of the following statements is true?
- Silicon conducts electricity better than aluminum.
- Sulfur is more electronegative than chlorine.
- The +1 oxidation state is common for sodium but not for aluminum.
- The ionic radius of Cl- is greater than that of S2-.
- The atomic radius of aluminum is greater than that of sodium.
19. Which of the following molecules has the longest bond?
- I2
- IBr
- ICl
- Cl2
- Br2
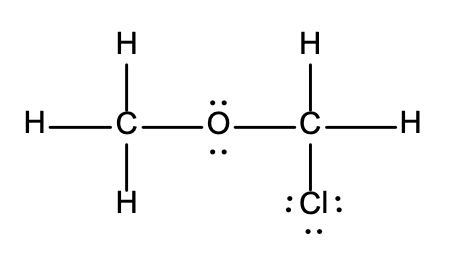
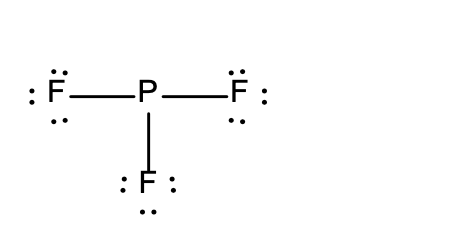
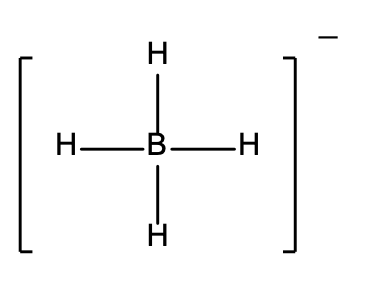
20. Which of the following Lewis structures is incorrect?
21. The following equation represents a fission reaction in which an isotope of uranium is bombarded with neutrons.
What must be the value of x in order to balance the equation?
10n + 23592U → 14156Ba + 9236Kr + x 10n
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
22. The concentration of H+ in stomach acid is about a million times greater than it is in pure water.
What is the approximate pH of stomach acid at 25°C?
- 1.0
- 1.5
- 2.0
- 3.0
- 5.5
23. The first six ionization energies of a particular element are shown in the graph below.
To which group of the periodic table does this element belong?
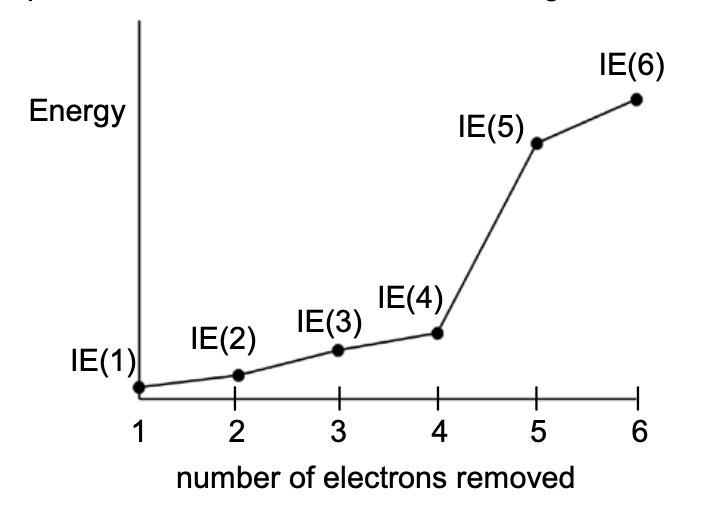
- group 1
- group 2
- group 13
- group 14
- group 15
24. Which of the following produces the greatest mass of metal upon reduction with one mole of electrons?
- Al3+
- Cu2+
- Pt2+
- Mg2+
- Ag+
25. A 10.0 L gas cylinder contains neon gas with a measured pressure of 65.0 kPa at 315 K.
The 10.0 L cylinder is then connected to an empty cylinder of unknown volume, and the neon gas expands to fill both cylinders.
If the final pressure is found to be 46.3 kPa at 315 K, then
what is the volume of the second cylinder?
- 4.04 L
- 13.0 L
- 14.0 L
- 1.87 L
- 7.12 L
26. Which of the following atoms, in their ground electronic states, does not have a half-filled subshell?
- Ga
- H
- Mn
- K
- As
27. What is the formula of the stable compound that contains only magnesium and phosphate ions?
- Mg2(PO4)3
- MgPO4
- Mg(PO4)2
- Mg5PO4
- Mg3(PO4)2
28. Suppose 10.0 mL of a 1.0 mol/L solution of HCl is diluted with water to a final volume of 1.0 L.
What happened to the pH of the solution?
- The pH decreases by 10 units.
- The pH increases by 10 units.
- The pH decreases by 2 units.
- The pH increases by 2 units.
- The pH changes by less than 1 unit.
29. How many moles of Br− are in 250.0 mL of a solution that is 0.148 mol/L with respect to NaBr and 0.212 mol/L with respect to CaBr₂?
- 0.572 mol
- 0.090 mol
- 0.143 mol
- 0.360 mol
- 0.427 mol
30. Select the one correct or the one incorrect statement.
- Ionization energies generally decrease from left to right across a row in the periodic table.
- Ionization energies generally decrease from top to bottom in a vertical group of the periodic table.
- Atomic sizes generally increase from top to bottom in a vertical group of the periodic table.
- The atomic radius generally decreases from left to right across a row in the periodic table.
- The second ionization energy of an element is always larger than the first ionization energy.
31. Deviations from ideal gas behaviour are most evident for a gas at
- high temperature and high pressure
- low temperature and low pressure
- high temperature and low pressure
- low temperature and high pressure
- high temperature in a large volume
32. The partial pressures of three gases in a 5.00 L cylinder at 1000°C are as follows.
CO₂: 239 kPa H₂: 72 kPa H₂O: 106 kPa
How many moles of CO₂ are in the cylinder?
- 0.203 mol
- 0.144 mol
- 0.113 mol
- 0.261 mol
- 0.355 mol
33. A sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) solution has a density of 1.29 g/mL and is 98% by mass H₂SO₄.
What is the molar concentration of this solution?
- 0.38 mol/L
- 0.49 mol/L
- 0.98 mol/L
- 5.0 mol/L
- 10.0 mol/L
Molar masses, in g/mol
-
H, 1.008
-
O, 16.00
-
S, 32.07
34. In the structure below, X represents an unidentified element
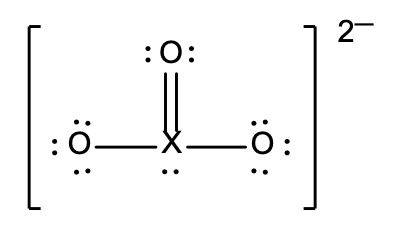
What is the possible identity of X?
- carbon, C
- nitrogen, N
- sulfur, S
- phosphorus, P
- chlorine, Cl
35. A particular airship (a zeppelin or blimp) uses C₈H₁₆ as fuel
C₈H₁₆ + 12 O₂ → 8 CO₂ + 8 H₂O
To counterbalance the weight loss of fuel used in the operation of the airship, part of the water contained in the exhaust gases must be condensed and retained.
The remainder of the water and the CO₂ are vented to the atmosphere.
If the mass of water retained exactly offsets the mass of fuel burned, what percentage of the water is retained?
- 22%
- 39%
- 11%
- 61%
- 78%
36. In the following structures for four different carbon-hydrogen compounds:
A carbon atom exists wherever a line ends or meets another line, and the number of H atoms needed to complete each carbon atom's four bonds are assumed to be present.
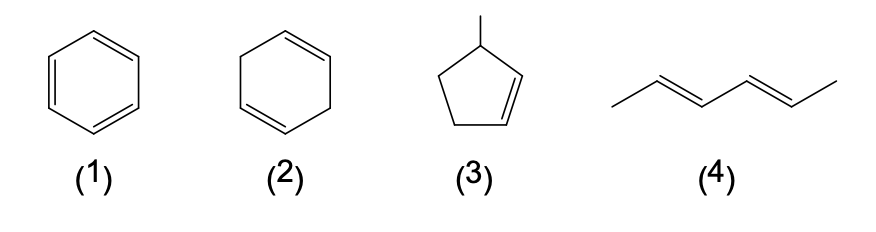
Which two compounds are isomers with the formula C6H10?
- (1) and (2)
- (2) and (3)
- (3) and (4)
- (2) and (4)
- (1) and (3)
37. Refer to the information and structures given in question 36.
In which compound are all the carbon-carbon bond lengths the same?
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- (4)
- none of the above
38. In a well-insulated container, an endothermic chemical reaction takes place.
When the reaction is done, the temperature of the contents will be
- higher than before the reaction began
- higher or lower than at the start of the reaction, depending on the heat capacities of the substances involved
- the same as before the reaction began
- lower than before the reaction began
- independent of the heat capacities of the substances involved
39. To a weighed, clean and dry 1.000 L volumetric flask is added some pure NH4Cl.
The flask is reweighed. Then distilled water is added to dissolve the NH4Cl, and finally enough water is added, with stirring, to bring the solution to the 1.000 L mark. The flask is reweighed.
Data are shown below.
-
Mass of clean and dry 1.000 L flask: 224.3 g
-
Mass of flask plus NH4Cl: 280.1 g
-
Mass of flask plus NH4Cl plus water: 1239.5 g
Which of the following statements concerning the resulting solution is correct?
- The molar concentration of NH4Cl is 5.23 mol/L.
- The density of the solution is 1.24 g/mL.
- The solution is 22.6% NH4Cl by mass.
- All of A, B and C are true.
- None of A, B and C are true.
40. One of two identical balloons contained carbon dioxide (CO2 44 g mol-1) and the other contained hydrogen (H2 2.0 g mol-1).
If it took 24 hours for all of the H2 to escape from its balloon,
how long did it take for all of the CO2 to escape? (Choose the closest value.)
Hint: For a sample of gas at a fixed temperature T, the average speed of molecules is inversely proportional to m1/2, where m is the molecular mass.
- 530 hours
- 110 hours
- 230 hours
- 1 hour
- 5 hours
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 2011 DATA SHEET
DETACH CAREFULLY
Additional interactive periodic tables
Constants
NA = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1
R = 0.08206 atm L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 kPa L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1
Kw = 1.0 \times 10^{-14} (at 298 K)
F = 96 485 C mol-1
Conversion factors
1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg
0oC = 273.15 K
Equations
PV = nRT
k t1/2 = 0.693
pH = pKa + log ([base]/[acid])
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM © 2011 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO