UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
8 MAY 2008
TIME: 75 MINUTES
This exam is being written by several thousand students. Please be sure that you follow the instructions below.
We'll send your teacher a report on your performance. Top performers are eligible for a prize. The names of the top 200 students will be published in the September issue of Chem 13 News.
- Print your name here: _________________________
- Print your school name and city on your STUDENT RESPONSE sheet.
- Select, and enter on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet, one of the following CODE numbers:
- Code 1 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a nonsemestered school
- Code 2 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a semestered school
- Code 3 Ontario, Grade 12 Chemistry already completed
- Code 4 Any other Ontario student
- Code 5 Manitoba or Saskatchewan high school student
- Code 6 Québec high school student
- Code 7 Québec CEGEP student
- Code 8 Alberta or British Columbia high school student
- Code 9 New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, or Prince Edward Island high school student
- Code 10 Northwest Territories, Nunavut, or Yukon high school student
- Code 11 High school student outside Canada
- Code 12 Teacher
- Print your name (last name, first name and optional middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed name.
- Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet.
- Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number.
- Mark only one answer for each question.
- Questions are all of the same value.
- There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer.
- Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval.
Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the sheet white again.
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
1. Which of the following statements about the group 17 elements is false?
- The ionization energy decreases down the group.
- The group contains both metals and non-metals.
- Electronegativity decreases down the group.
- The melting point increases down the group.
- The most common ion formed by these elements is X-.
2. Which of the following has the highest melting point?
- I2(s)
- C60(s)
- NaCl(s)
- LiF(s)
- Xe(s)
3. The acid ionization constant for HNO2 is Ka = 4.5 × 10-4 at 298 K.
What is the pH of 0.100 mol L-1 HNO2(aq) at 298 K?
(Choose the closest value.)
- 1.00
- 2.17
- 1.67
- 3.23
- 6.53
4. A 0.100 mol L-1 solution of which of the following salts has the highest pH at 298 K?
- NaF
- NaIO3
- NaCN
- NH4F
- NH4IO3
Ionization constants (at 298 K)
-
HIO3, Ka = 1.7 × 10-2
-
HF, Ka = 6.3 × 10-4
-
HCN, Ka = 6.2 × 10-10
-
NH3, Kb = 1.8 × 10-5
-
H2O, Kw = 1.0 × 10-14
5. A solution is prepared by dissolving 4.50 grams of solid NaOH in 1.00 L of 0.100 mol L-1 HNO2(aq) at 298 K.
What is the pH of this solution? Assume that the final volume is 1.00 L.
- 7.00
- 1.90
- 2.45
- 12.10
- 13.05
Ionization constants (at 298 K)
-
HNO2, Ka = 4.5 × 10-4
-
H2O, Kw = 1.0 × 10-14
6. If 1.00 L of 0.100 mol L-1 HNO2(aq) is diluted with water to a final volume of 4.00 L, then which of the following statements regarding the new solution is true?
- The percent ionization of the acid decreases and the pH remains the same.
- The percent ionization of the acid increases and the pH decreases.
- The percent ionization of the acid increases and the pH increases.
- The percent ionization of the acid decreases and the pH decreases.
- The percent ionization of the acid increases and the pH remains the same.
7. Which of the following equilibria shifts to the left when the external pressure is increased and shifts to the right when the temperature is increased?
- N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 NO(g) ΔH > 0
- 2 H2O(g) ⇌ O2(g) + 2 H2(g) ΔH < 0
- PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g) ΔH > 0
- N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g) ΔH < 0
- 2 CO2(g) ⇌ 2 CO(g) + O2(g) ΔH > 0
Use the table of standard reduction potentials given below to answer questions 8 through 10.
| Half-Reaction | E° |
|---|---|
| Ag+(aq)+e-⇌ Ag(s) | +0.80 V |
| O2(g)+2H2O(l)+4e-⇌4OH-(aq) | +0.40 V |
| Cu2+(aq)+2e-⇌ Cu(s) | +0.34 V |
| 2H+(aq)+2e-⇌ H2(g) | 0.0 V |
| Sn2+(aq)+2e-⇌ Sn(s) | -0.14 V |
| Ni2+(aq)+2e-⇌ Ni(s) | -0.25 V |
| Fe2+(aq)+2e-⇌ Fe(s) | -0.41 V |
| Cr3+(aq)+3e-⇌ Cr(s) | -0.74 V |
| Zn2+(aq)+2e-⇌ Zn(s) | -0.76 V |
| 2H2O(l)+2e-⇌ H2(g)+2OH-(aq) | -0.83 V |
| Al3+(aq)+3e-⇌ Al(s) | -1.66 V |
8. Which of the following is the best reducing agent under standard conditions?
- Cu(s)
- Zn(s)
- Al3+(aq)
- Fe2+(aq)
- Ag(s)
9. The metal X dissolves in HCl(aq) but does not react in pure water, even its powdered form.
It is a better reducing agent than Ni(s). It forms an oxide with the formula X2O3.
What is X?
- silver, Ag
- copper, Cu
- zinc, Zn
- aluminum, Al
- chromium, Cr
10. Sacrificial anodes are attached to the hulls of ships to protect the iron (Fe) in the hull from corrosion.
Which of the following metals could be used as a sacrificial anode for protecting the iron hull of a ship?
- nickel, Ni
- zinc, Zn
- tin, Sn
- copper, Cu
- silver, Ag
11. The phase diagram for carbon dioxide is shown below.
The temperature and pressure at the triple point (TP) and the critical point (CP) are shown.
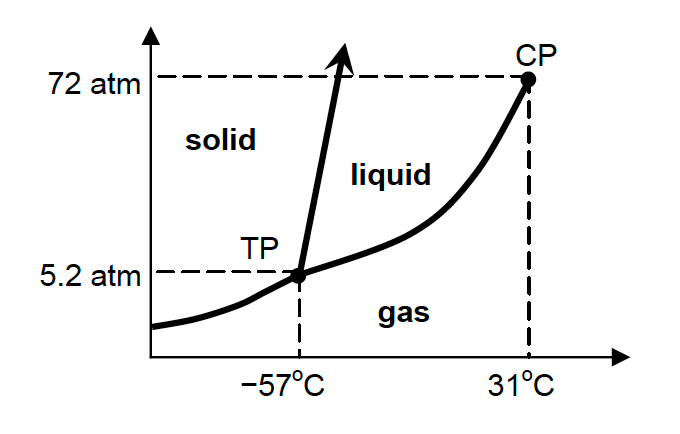
Which of the following accounts for the fact that liquid CO2 is not observed when a piece of solid CO2 (dry ice) is placed on a lab bench at 25°C and 1 atm?
- The triple point temperature is less than the critical point temperature.
- The critical temperature is greater than 25°C.
- The triple point temperature is less than 25°C.
- The critical pressure is greater than 1 atm.
- The triple point pressure is greater than 1 atm.
12. When 1.50 grams of a compound containing only carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen is burned completely in excess O2, 1.72 g CO2, 0.585 g NO and 1.23 g H2O are produced.
What is the empirical formula for the compound?
- C2H7O2N
- C2H14O2N
- CH7ON
- C2H7ON2
- CH7O2N
13. What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in benzene, C6H6?
- sp2 and sp3
- sp3 only
- sp, sp2 and sp3
- sp2 only
- sp only
14. How many structural isomers are there for C4H8?
- one
- two
- three
- four
- more than four
15. The reaction below was studied at 40°C using the method of initial rates.
Data are given in the table below.
S2O82-(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → 2 SO42-(aq) + I2(s)
| run | [S2O82-] (in mol L-1) |
[I-] (in mol L-1) |
Initial Rate (in mol L-1 s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.10 | 0.020 | 3.5×10-4 |
| 2 | 0.020 | 0.20 | 1.4×10-3 |
| 3 | 0.020 | 0.40 | 2.8×10-3 |
What are the correct value and units of the rate constant, k?
- 0.35 mol L-1 s-1
- 3.5 mol L-1 s-1
- 0.35 mol-1 L s-1
- 0.35 mol-2 L2 s-1
- 1.8×102 mol-1 L s-1
16. For the reaction below, ΔH° = -879.6 kJ.
3 N2O(g) + 2 NH3(g) → 4 N2(g) + 3 H2O(g)
Given that ΔHf° = -45.9 kJ mol-1 for NH3(g) and ΔHf° = -241.8 kJ mol-1 for H2O(g), what is ΔHf° for N2O(g)?
- 684 kJ mol-1
- -504 kJ mol-1
- -684 kJ mol-1
- 82.0 kJ mol-1
- The answer cannot be determined with the information provided.
17. The following figure shows the contents and pressures of three vessels of gas which are joined by a connecting tube.

Three connected vessels of gas with the following contents, pressures and volumes: He, 0.75 atm, 1.0 L; Xe, 0.45 atm, 2.5 L; Ar, 1.20 atm, 1.0 L. The valve is located at the middle Xe vessel.
After the valves on the vessels are opened, the final pressure is measured and found to be 0.675 atm.
What is the total volume of the connecting tube?
All vessels are at a constant temperature of 25°C.
- 0.53 L
- 0.056 L
- 0.094 L
- 0.040 L
- 0.023 L
18. At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant for the reaction below is Kp = 0.100.
P4(g) ↔ 2 P2(g)
In an experiment, some P4 gas was added to an empty reaction vessel and then the vessel was quickly sealed.
The total pressure at equilibrium was 1.00 atm.
What was the initial pressure of P4 used in this experiment?
- 1.00 atm
- 0.730 atm
- 0.752 atm
- 0.865 atm
- 0.667 atm.
19. In acidic aqueous solution, zinc metal is oxidized to Zn2+.
The net ionic equation for the reaction is given below.
Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
In an experiment, 5.0 grams of Zn(s) were added to 100 mL of 1.0 mol L-1 HCl(aq).
Which of the following changes to the procedure would not affect the initial rate of the reaction?
- warming the HCl solution before adding the zinc
- using zinc powder instead of zinc granules
- using 50 mL of 1.0 mol L-1 HCl(aq)
- using 200 mL of 0.50 mol L-1 HCl(aq)
- using 100 mL of 1.0 mol L-1 H2SO4(aq)
20. Which of the following groups of ions and atoms is comprised of species having exactly the same ground state electron configuration?
- Al3+, O2-, Ne, Cl-
- Ca, Ti2+, Cl-, S2-
- H-, He, Li, Be2+
- Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe
- Ca2+, Ti4+, Cl-, S2-
21. Proteins are polymers of which kind of acids?
- amino acids
- strong acids
- binary acids
- inorganic acids
- lactic acids
22. In separate experiments, a 50.0-mL sample of each of the two solutions listed below is titrated with 0.10 mol L-1 NaOH(aq).
0.10 mol L-1 HCl(aq), pH = 1.0
0.10 mol L-1 HCN(aq), pH = 5.1
Which of the following statements is true?
- For both titrations, the pH at the equivalence point is 7.00.
- It takes a greater volume of the NaOH solution to reach the equivalence point for the titration of the HCl solution than it does for the titration of the HCN solution.
- For both titrations, the pH at the equivalence point is greater than 7.00.
- HCN is a stronger acid than HCl.
- For both titrations, it takes 50.0 mL of the NaOH solution to reach the equivalence point.
23. At high temperatures, sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO3, decomposes according to the chemical equation given below.
2 NaHCO3(s) ⇌ Na2CO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
What is the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction?
- Kc = [H2O][CO2][Na2CO3] / [NaHCO3]
- Kc = [H2O][CO2][Na2CO3] / [NaHCO3]2
- Kc = [H2O][CO2]
- Kc = [NaHCO3]2 / ([H2O][CO2][Na2CO3])
- Kc = 1 / ([H2O][CO2])
24. Which of the following statements is always true?
- A nonelectrolyte is ionized completely in aqueous solution.
- Most ionic compounds of the Group 1 elements are insoluble.
- A 1 mol L-1 solution of NH3(aq) is a better conductor of electric current than a 1 mol L-1 solution of HCl(aq).
- A weak acid is partially ionized in aqueous solution.
- Cl- will precipitate Na+ from solution.
25. Given the data below, what is the bond dissociation energy for the H-Cl bond?
-
H-H bond dissociation energy = 432 kJ mol-1
-
Cl-Cl bond dissociation energy = 244 kJ mol-1
-
ΔHf° for HCl = -92 kJ mol-1
- 430 kJ mol-1
- 384 kJ mol-1
- 123 kJ mol-1
- 92 kJ mol-1
- 767 kJ mol-1
26. Of the following organic compounds, which is least soluble in water at 298 K?
- methanol, CH3OH
- ethanol, CH3CH2OH
- dimethyl ether, H3COCH3
- ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH
- ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
27. The temperature-time graph is shown below for heating H2O at a constant rate of 1.00 kJ s-1.
What does the line segment DE represent?
- warming of ice
- fusion
- warming of liquid
- vaporization
- condensation
28. The unbalanced chemical equation for the oxidation of Br- by MnO4- is given below.
The reaction occurs in aqueous acidic solution.
Br- + MnO4- → Br2 + Mn2+
How many moles of MnO4- are required to oxidize exactly 1.0 mol Br-?
- 1.0 mol
- 0.2 mol
- 5.0 mol
- 0.1 mol
- 10 mol
29. Which of the following is the best choice to measure accurately 22.5 mL of a solution?
- a 50 mL buret
- a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask
- a 50 mL beaker
- a 50 mL graduated cylinder
- a 50 mL volumetric pipet
30. Solid NH4NO3 is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH, and the solution is warmed.
Which of the following gases is produced?
- nitrogen, N2
- oxygen, O2
- dinitrogen oxide, N2O
- hydrogen, H2
- ammonia, NH3
31. Which one of the following solutions does not conduct electricity at 25°C?
- 0.10 mol L-1 CH3CH2OH(aq)
- 0.10 mol L-1 H2SO4(aq)
- 0.10 mol L-1 CH3COOH(aq)
- 0.10 mol L-1 HNO3(aq)
- 0.10 mol L-1 NH3(aq)
32. In which of the following compounds is the oxidation state of chlorine equal to +5?
- HCl
- ClF3
- HClO3
- PCl5
- HClO2
33. The structure of which of the following is not a hybrid of two or more equivalent resonance structures?
- CO32-
- PO43-
- C6H6
- O3
- C2H4
34. For the reaction 2 HBr + ½ O2 → H2O + Br2, the following mechanism has been proposed.
-
HBr + O2 → HOOBr fast
-
HOOBr + HBr → 2 HOBr slow
-
HOBr + HBr → H2O + Br2 fast
What is the predicted rate law for the overall reaction?
- Rate = k [HBr]2 [O2]
- Rate = k [HBr]2 [O2]½
- Rate = k [HBr] [O2]
- Rate = k [HBr] [O2]2
- Rate = k ([H2O][Br2] / ([HBr]2 [O2]½))
35. Which of the following substances is the most soluble in hexane, C6H14(l)?
- NaCl
- Cl2
- CH3Cl
- HCl
- CaCl2
36. Which oxide of nitrogen is 36.8% N by mass?
- N2O4
- NO
- N2O3
- NO2
- N2O
37. A student drew the following Lewis structures for NO, CO, NH₃ and BH₃.
Which of the following structures is (are) correct?
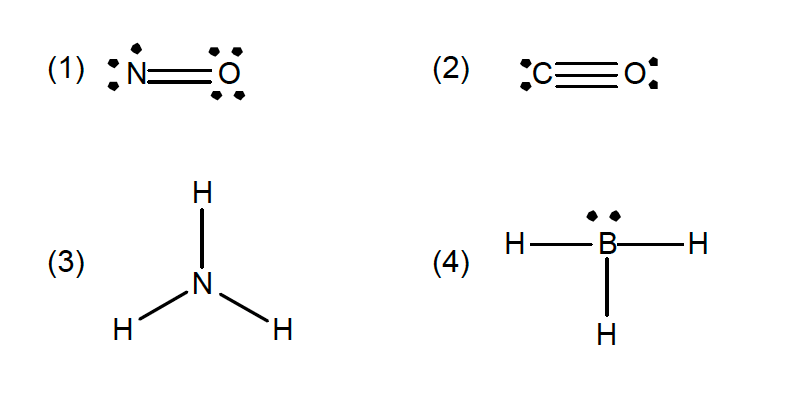
- (1) only
- (3) and (4)
- (1) and (2)
- (2) and (3)
- (3) only
38. The reaction N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) → 2 NH₃(g) is exothermic.
The reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium in a closed vessel.
Which of the following will lead to an increase in the number of moles of ammonia in the equilibrium mixture?
- (1) only
- (1) and (2) only
- (2) and (3) only
- (3) and (4) only
- (1), (2) and (4)
39. What is the maximum mass of nickel metal that can be deposited from an aqueous solution of Ni(NO₃)₂ by the passage of three moles of electrons?
- 29 g
- 39 g
- 59 g
- 88 g
- 176 g
40. Ethanoic acid, CH₃COOH, is a weak acid in water.
What happens when 0.01 mol of HCl are added to a 0.1 mol L⁻¹ solution of ethanoic acid?
- The pH of the solution increases and the percent ionization of ethanoic acid increases.
- The pH of the solution decreases and the percent ionization of ethanoic acid increases.
- The pH of the solution decreases and the percent ionization of ethanoic acid decreases.
- The pH of the solution increases and the percent ionization of ethanoic acid decreases.
- The weak acid is neutralized by the strong acid and the pH of the solution is 7.00.
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 2010 DATA SHEET
DETACH CAREFULLY
Additional interactive periodic tables
Constants
NA = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1
R = 0.08206 atm L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 kPa L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1
Kw = 1.0 \times 10^{-14} (at 298 K)
F = 96 485 C mol-1
Conversion factors
1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg
0oC = 273.15 K
Equations
PV = nRT
k t1/2 = 0.693
pH = pKa + log ([base]/[acid])
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM © 2010 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO