UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
14 MAY 2009
TIME: 75 MINUTES
This exam is being written by several thousand students. Please be sure that you follow the instructions below.
We'll send your teacher a report on your performance. Top performers are eligible for a prize. The names of the top 200 students will be published in the September issue of Chem 13 News.
- Print your name here: _________________________
- Print your school name and city on your STUDENT RESPONSE sheet.
- Select, and enter on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet, one of the following CODE numbers:
- Code 1 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a nonsemestered school
- Code 2 Ontario, now studying Grade 12 Chemistry in a semestered school
- Code 3 Ontario, Grade 12 Chemistry already completed
- Code 4 Any other Ontario student
- Code 5 Manitoba or Saskatchewan high school student
- Code 6 Québec high school student
- Code 7 Québec CEGEP student
- Code 8 Alberta or British Columbia high school student
- Code 9 New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, or Prince Edward Island high school student
- Code 10 Northwest Territories, Nunavut, or Yukon high school student
- Code 11 High school student outside Canada
- Code 12 Teacher
- Print your name (last name, first name and optional middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed name.
- Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet.
- Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number.
- Mark only one answer for each question.
- Questions are all of the same value.
- There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer.
- Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval.
Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the sheet white again.
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
1. In the third period of the elements, how do the atomic radii of the elements vary?
- The radii increase steadily from Na to Ar.
- The radii increase from Na to Al and decrease from Al to Ar.
- There is no regular pattern.
- The radii decrease from Na to S and increase from S to Ar.
- The radii decrease steadily from Na to Ar.
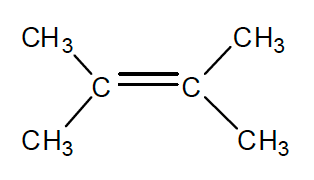
2. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
- CH3CCl=CClCH3
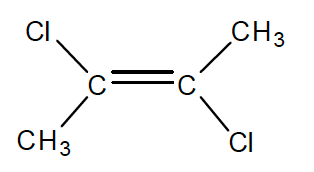
- (CH3)2C=C(CH3)2
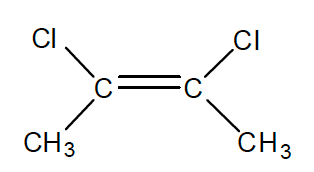
- CH3C≡CCH3

- ClC≡CCl
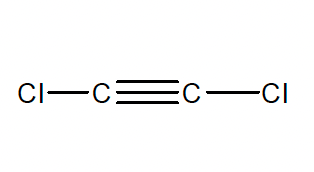
- (CH3)2C=CHCH3
3. Nitrous acid, HNO2, is a weak acid in water. Which of the following statements concerning NO2- is true?
Ka=7.2×10-4 at 298 K for HNO2.
- NO2- is a weak base.
- NO2- is a strong base.
- NO2 is a weak acid.
- NO2- is a strong acid.
- NO2- is neither an acid nor a base.
4. How many moles of NaOH should be added to 1.0 L of 0.10 mol L-1 HCOOH(aq) to obtain a solution having a final pH of 4.0 at 298 K?
Assume no change in volume. (Choose the closest value.)
Ka=1.8×10-4 at 298 K for HCOOH.
- 0.018 mol
- 1.8 mol
- 0.26 mol
- 0.064 mol
- 0.0099 mol
5. Which of the following molecules do not form hydrogen bonds amongst themselves?
- CH3COOH
- H2O2
- CH3OCH3
- HF
- CH3CH2OH
6. The reaction below reaches equilibrium in a closed reaction vessel.
4 HCl(aq) + MnO2(s) ΔH<0 ⇌ Cl2(g) + 2 H2O(l) + Mn2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
Which of the following actions increases the mass of Cl2(g) in the equilibrium mixture?
- adding some MnO2(s)
- increasing the temperature
- adding some MnCl2(s)
- decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel
- adding something that precipitates Mn2+
Use the following information and diagram to answer questions 7-10.
A galvanic cell is constructed by placing a strip of zinc into a 1.0 mol L-1 solution of zinc nitrate and a strip of aluminum into a 1.0 mol L-1 solution of aluminum nitrate. The two metal strips are connected to a voltmeter by wires and a salt bridge connects the solutions. (See the diagram below.) The temperature is 25 °C. The following standard reduction potentials apply:
Al3+(aq) + 3e- → Al(s) E° = -1.67 V
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) E° = -0.76 V
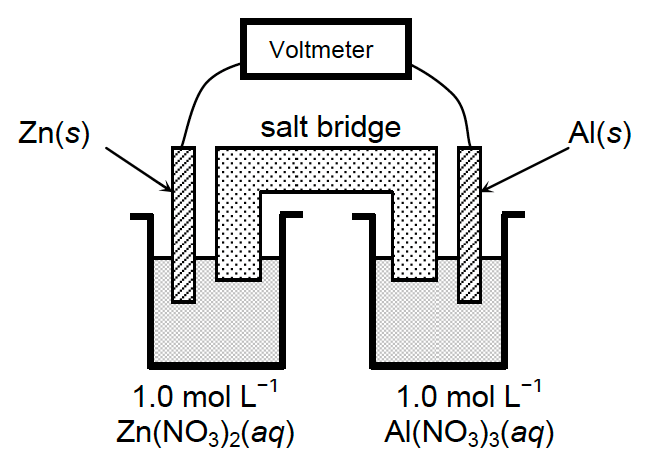
7. What is E° for the cell described above?
- 0.15 V
- 0.91 V
- 2.43 V
- 3.49 V
- 6.53 V
8. In the cell described above, where does reduction occur?
- at the aluminum electrode
- at the zinc electrode
- at the voltmeter
- in the salt bridge
- in the aluminum nitrate solution
9. Considering the standard reduction potentials given in the box on the right,
which of the following is the strongest reducing agent under standard conditions?
- Al(s)
- Al3+(aq)
- Zn(s)
- Zn2+(aq)
- impossible to determine
10. What is Ecell equal to when the cell described in the box reaches equilibrium at 25 °C?
- -2.43 V
- +5.62 V
- 0 V
- 1.06 V
- none of the above
11. A compound is 54.6% C, 36.2% O and 9.2% H by mass. What is the empirical formula of the compound?
- CH2O
- C2H4O
- C3H6O2
- C4H4O
- C6H6O
12. What is the pH of a 1.25×10-7 mol L-1 HCl(aq)?
- 6.90
- 6.74
- 7.00
- 6.67
- less than 6.67
13. Which of the following statements is true?
- A single covalent bond consists of a single delocalized electron.
- For a bond formed between a given pair of atoms, the bond dissociation energy increases as the bond order decreases.
- The bond dissociation energy for a C=C bond is twice that of a C-C bond.
- A polar covalent bond results from the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another.
- none of the above
14. How many isomers are there for C5H12?
- one
- two
- three
- four
- more than four
15. The enthalpy change for the reaction below is ΔH = -58 kJ (per mole of N2O4 formed).
2NO2(g) + 2 I-(aq) ⇌ 2 SO42-(aq) + I2(s)
If k1 and k-1 are the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions, respectively, and
Kc is the equilibrium constant for the reaction as written, then
what effect does increasing the temperature have on the values of k1, k-1, and Kc?
- k1 increases, k-1 decreases, Kc increases
- k1 increases, k-1 increases, Kc increases
- k1 increases, k-1 increases, Kc decreases
- k1 increases, k-1 decreases, Kc decreases
- k1 decreases, k-1 decreases, Kc decreases
16. Consider the thermochemical equations below.
C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) ΔH° = -1411 kJ (per mol C2H4)
C2H4(g) + H2O(l) → C2H5OH(l) ΔH° = -44 kJ (per mol C2H4)
What is ΔH° for the following reaction? All the answers below are for the combustion of one mole of C2H5OH.
C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l)
- -1089 kJ
- 632 kJ
- -1455 kJ
- -1733 kJ
- -1367 kJ
17. A 10.0-L gas cylinder contains neon gas with a measured pressure of 5.50 atm at 298 K.
The 10.0-L cylinder is then connected to an empty gas cylinder of unknown volume, and the neon gas expands to fill both cylinders.
If the final pressure is found to be 3.76 atm at 298 K, then what is the volume of the second cylinder?
- 14.6 L
- 6.52 L
- 10.0 L
- 4.63 L
- 9.26 L
18. Which of the following correctly describes what happens when aqueous solutions of ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3, and potassium bromide, KBr, are mixed?
- Br- neutralizes NH4+.
- K2CO3(s) precipitates.
- HBr is formed.
- NH4Br(s) precipitates.
- none of the above
Use the information and diagram below to answer questions 19-21.
A 40.0-mL sample of a weak monoprotic acid, HA, is titrated with 0.20 mol L-1 NaOH(aq). The titration curve is shown below.
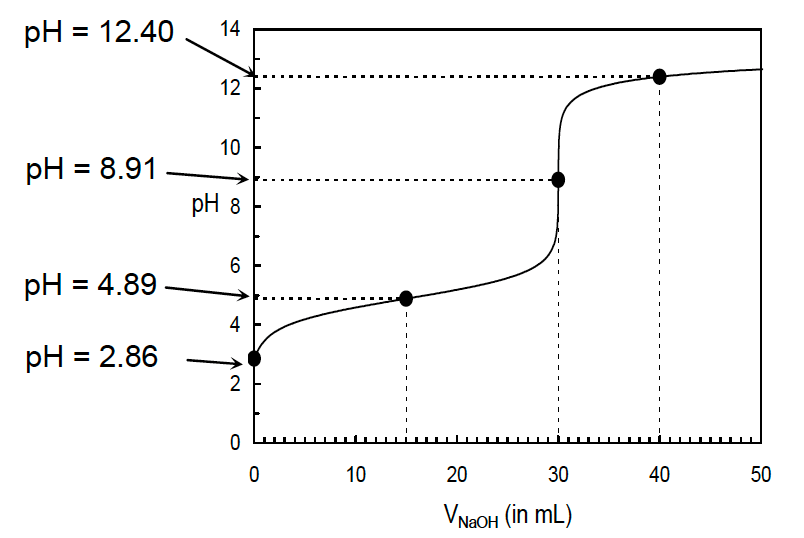
19. For the titration described above, which of the following is true at the equivalence point?
- [HA]=[Na+]
- [A-]=[HA]
- [Na+]=[A-]
- [H+]=[OH-]
- [A-]=[H+]
20. Based on the titration curve above, what was the concentration of the original sample solution (i.e. before the titration started)?
- 0.63 mol L-1
- 0.15 mol L-1
- 0.24 mol L-1
- 0.067 mol L-1
- 0.20 mol L-1
21. Based on the titration curve above, what is the ionization constant (Ka) for the acid, HA?
- 10-12.40
- 10-8.91
- 10-4.89
- 10-2.86
- 10+2.86
22. How many unpaired electrons are there in the nickel (Ni) atom in its ground state electron state?
- 5
- 4
- 6
- 2
- 0
23. Equal volumes of 0.1 mol L-1 HCl(aq) and 0.1 mol L-1 HF(aq) are titrated in separate experiments with 0.1 mol L-1 NaOH(aq).
Which of the following would be equal for both titrations?
- the initial pH (i.e. the pH before any NaOH is added)
- the pH when half the acid has been neutralized (i.e. the pH at the half-neutralization point)
- the pH at the equivalence point
- the volume of NaOH required to reach the equivalence point
- none of the above
24. For the reaction below, Kc = 7.8×108.
What is the equilibrium concentration NH3 when 1.00 mol each of Zn(NO3)2 and NH3 are dissolved in water to make 1.0 L of solution?
Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) ⇌ Zn(NH3)42+(aq)
- 0 mol L-1
- 1.3×10-9 mol L-1
- 0.75 mol L-1
- 0.25 mol L-1
- 4.5×10-3 mol L-1
25. Which of the following molecules is polar?
- CS2
- N2O
- CCl4
- PF5
- SO3
26. Consider the compounds NaCl, AgCl and CO2 in terms of their solubilities in water.
Which of these compounds exhibits an increase in solubility if the temperature is lowered and the pressure is increased?
- NaCl only
- AgCl only
- CO2 only
- NaCl and AgCl
- NaCl, AgCl and CO2
27. When a 1.00 mol L-1 solution of M2+(aq) is electrolyzed with a current of 2.5 amperes for 0.2 hours, 0.485 g of M(s) are deposited.
What is the identity of M? (Note: 1 ampere = 1 C s-1)?
- Cr
- Rh
- Na
- Mg
- Ag
28. Iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3, reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce only water and a salt.
What is the formula of the salt?
- FeCl3
- FeCl2
- FeCl
- Fe2Cl3
- FeCl
29. The unbalanced chemical equation for the oxidation of Zn by NO3- is given below.
The reaction occurs in aqueous basic solution.
Zn + NO3- → Zn(OH)42- + NH3
How many moles of NO3- are required to oxidize exactly one mole of Zn?
- 1 mol
- ¼ mol
- 4 mol
- 8 mol
- ⅛ mol
30. Two students each made four measurements of the mass of an object.
Their results are shown in the table below
| Measurements: | Student A | Student B |
|---|---|---|
| 51.6 g | 50.1 g | |
| 50.8 g | 49.6 g | |
| 52.2 g | 51.0 g | |
| 50.2 g | 49.4 g | |
| Average: | 51.3 g | 50.0 g |
If the exact mass of the object is 51.0 g, then which of the following statements is true?
- Student A's results are more accurate and more precise.
- Student B's results are more accurate and more precise.
- Student A's results are more accurate but less precise.
- Student B's results are more accurate but less precise.
- The two sets of results are equally precise.
31. Which of the following compounds displays the greatest ionic character in its bonds?
- NO2
- CO2
- H2O
- NH3
- F2O
32. What is the oxidation state of oxygen in FOCN? The molecular structure of FOCN is shown below.
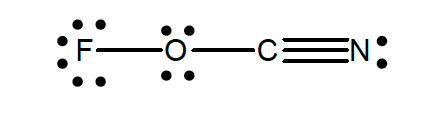
- zero
- +2
- -2
- +1
- -1
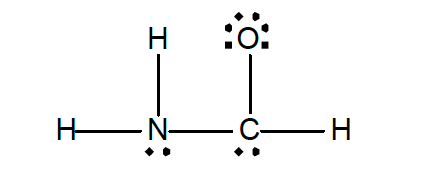
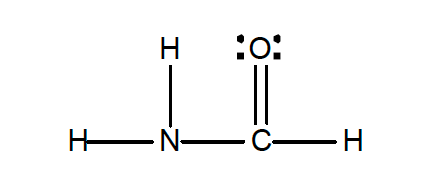
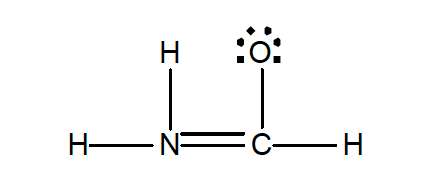
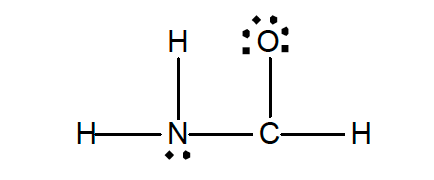
33. Experiment shows that in the formamide molecule, H2NCHO, the H-N-H angle is 119° and the N-C-O angle 124°.
Which of the following structures is an acceptable structure for H2NCHO and is consistent with the experimentally-bond angles?
34. Which of the following best describes the bonding in the N2 molecule?
- one σ bond and one π bond
- two σ bonds and one π bond
- two π bonds
- three σ bonds
- one σ bond and two π bonds
35. When building up the electron configuration of a neutral atom, which orbital fills immediately after the 5s orbital?
- 4d
- 4f
- 5p
- 6s
- 5d
36. What is the formula of perovskite?
Perovskite is a mineral containing Ca, O and Ti. The smallest repeating unit in the structure of perovskite is shown below.
(There is a single titanium atom at the centre of the cube.)
By considering the total number of atoms of each type that lie inside the cube below, determine the formula of perovskite.
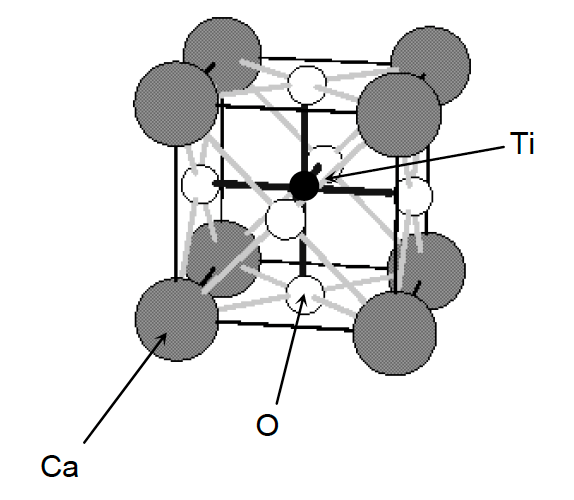
- CaOTi
- CaO2Ti
- Ca8O8Ti
- Ca2O3Ti
- CaO3Ti
37. Consider the Lewis structure shown below for the polyatomic ion, EOF₂⁻.
The central atom, E, is an unidentified element.
Which of the following atoms could E represent?
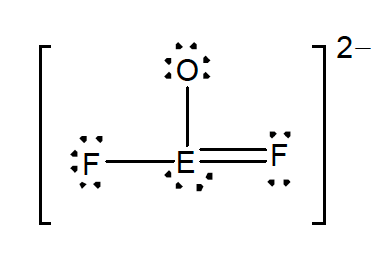
- oxygen (O)
- sulfur (S)
- bromine (Br)
- nitrogen (N)
- xenon (Xe)
38. Consider the following reaction mechanism.
(CH₃)₃C⁺ + N₃⁻ → (CH₃)₃CN₃
(CH₃)₃CBr ↔ (CH₃)₃C⁺ + Br⁻
According to this mechanism, (CH₃)₃C⁺ is
- a reaction product
- a reaction intermediate
- an activated complex
- a catalyst
- a Lewis base
39. What is the final temperature when 100.0 mL of water at 90.0 °C and 200.0 mL of water at 10.0 °C are mixed?
Assume no heat is lost to the surroundings. Choose the closest value.
Properties of water
density = 1.0 g mL⁻¹
specific heat = 4.18 J g⁻¹ °C⁻¹
heat of vaporization = 2260 J g⁻¹
- 40 °C
- 50 °C
- 70 °C
- 80 °C
- 100 °C
40. Which of the following is present in the greatest number in a dilute sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) solution?
- H₂SO₄ molecules
- HSO₄⁻ ions
- SO₄²⁻ ions
- H⁺ ions
- OH⁻ ions
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 2010 DATA SHEET
DETACH CAREFULLY
Additional interactive periodic tables
Constants
NA = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1
R = 0.08206 atm L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 kPa L K-1 mol-1 = 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1
Kw = 1.0 \times 10^{-14} (at 298 K)
F = 96 485 C mol-1
Conversion factors
1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg
0oC = 273.15 K
Equations
PV = nRT
k t1/2 = 0.693
pH = pKa + log ([base]/[acid])
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM © 2010 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO