Using AI to support real-time decision-making of FCEV2G stations
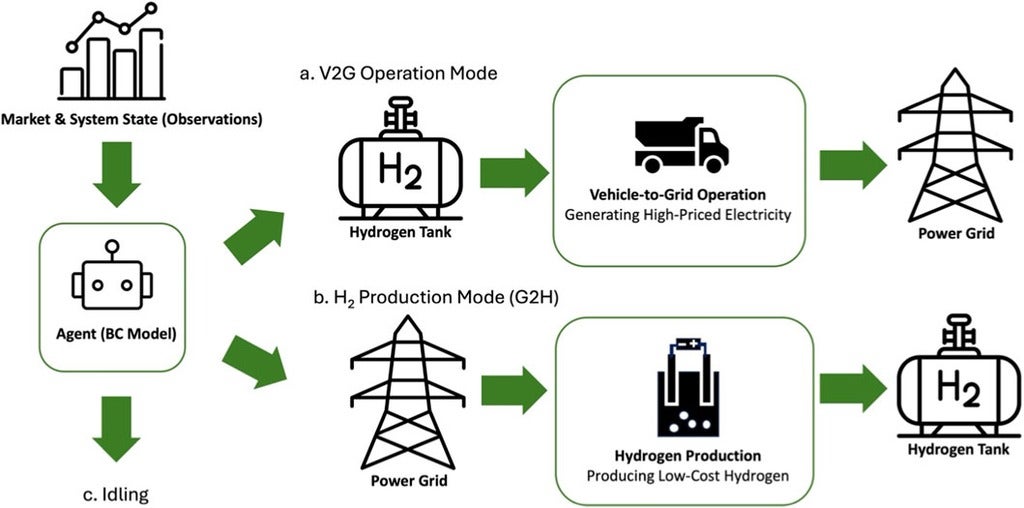
In a recent paper, we developed a supervised learning AI agent to support real-time decision-making for a fuel cell electric vehicle-to-grid (FCEV2G) station, specifically, whether to connect to the grid, produce hydrogen, or remain idle. The agent enabled the station to operate more effectively and capture most profit-making opportunities. While there is still significant room for improvement, this project is an interesting and promising first step for my group.
Congratulations to Arda Mert Çetin!