Agent-based model predictive control
Future mobility applications desire a carrier platform with ever-increasing demand for safety, reliability, and efficiency.
As a result, more mechatronics systems are used to enhance vehicular performances, and huge efforts have been devoted towards the development of a control system to coordinate all on-board mechatronic systems.
An integrated vehicular control scheme, which seeks an optimal distribution of control efforts by systematically considering all available actuators as well as constraints in a holistic model, has been developed in our previous endeavours. As more and more systems are incorporated into this centralized optimization scheme, the lack of flexibility and scalability with the current architecture are being observed.
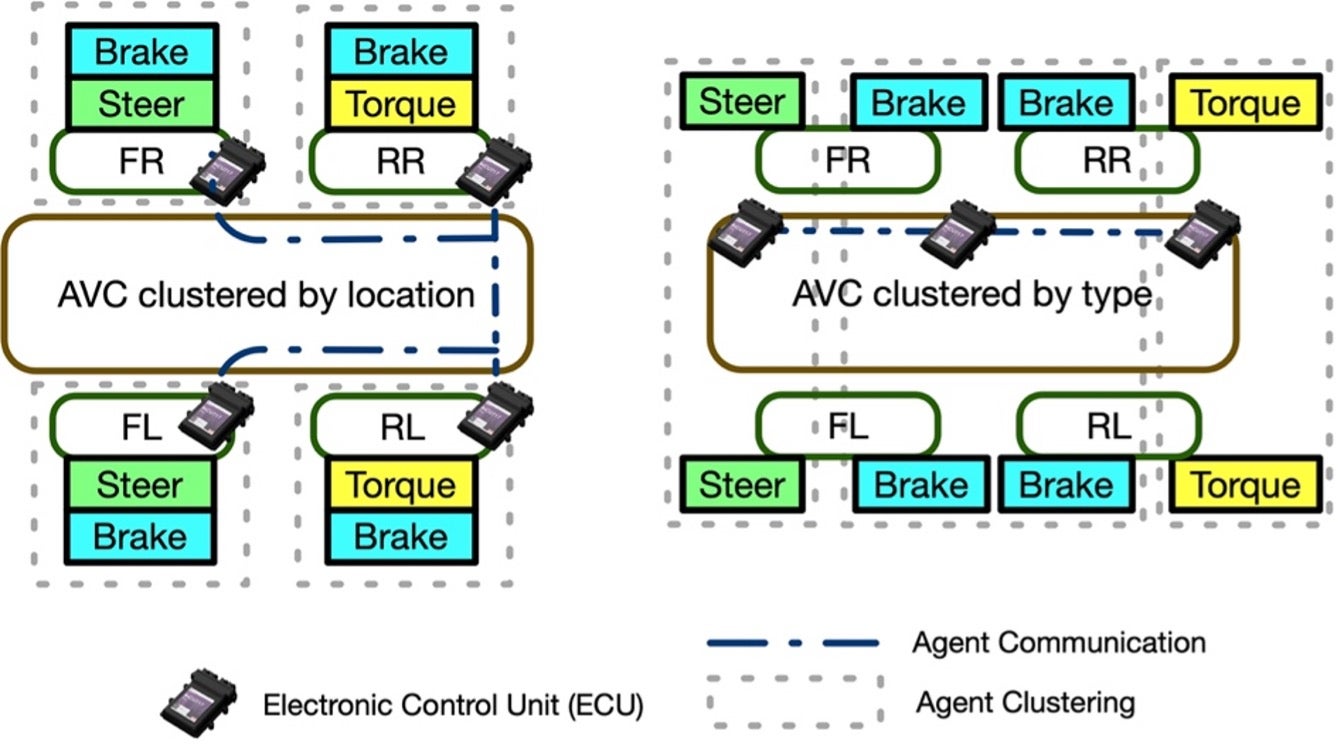
In this project, we intend to further extend the modularity and scalability of vehicular control systems by introducing agent-based model predictive controllers (AMPC). Different agent clustering schemes are analyzed for modular and production vehicle platforms, and a general decoupling technique for vehicle dynamics model is then introduced, which decomposes the original problem into multi-agent formulations.
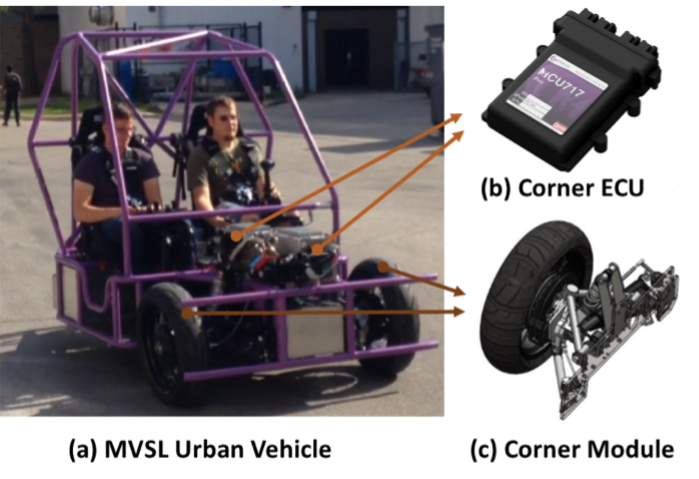
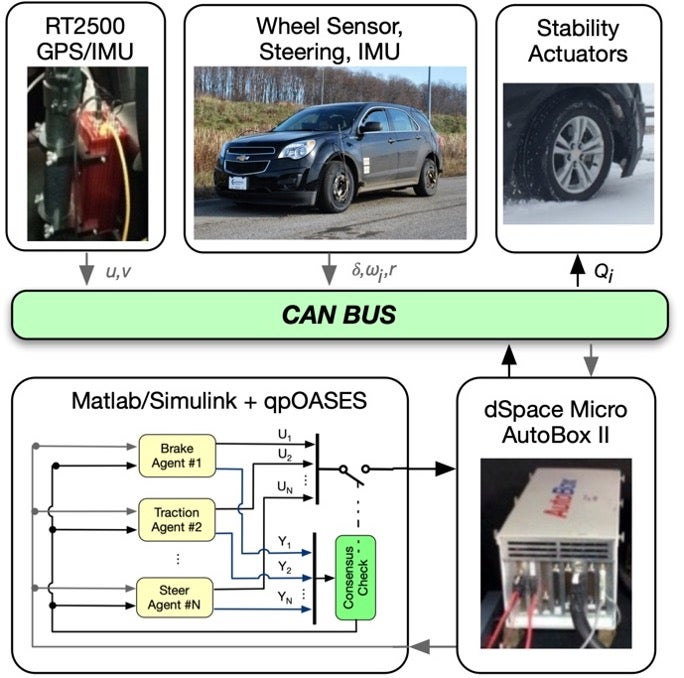
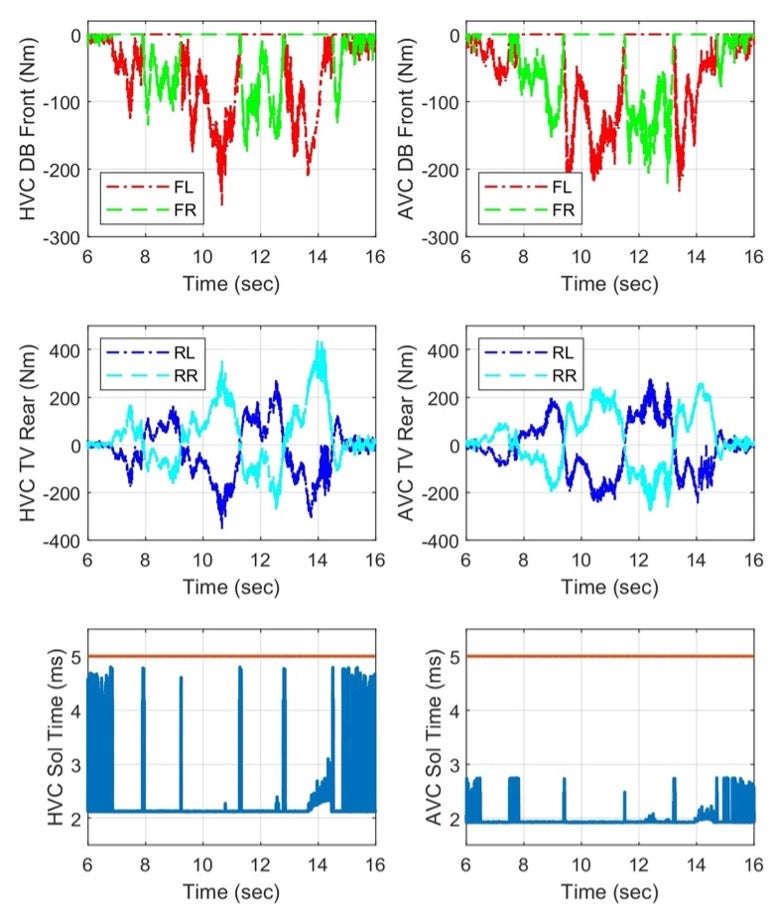
The resultant agent-based MPC has been implemented on a modular urban vehicle as well as an all-wheel-drive Equinox platform. The experimental results show that, the proposed agent-based MPC is more flexible and computationally efficient in handling vehicle active safety problem while gives no compromise to control performances compared to their holistic-formulated counterparts.
 |
|
Fig.1. Different agent clustering schemes |
 |
 |
|
(a) Modular Urban Vehicle at MVSL |
(b) All-wheel-drive Equinox |
|
Fig.2. Implementation of agent based MPC on different platforms |
|
 |
|
Fig.3. Experimental comparison between holistic and agent-based vehicle control |