Kral's Goldenrod
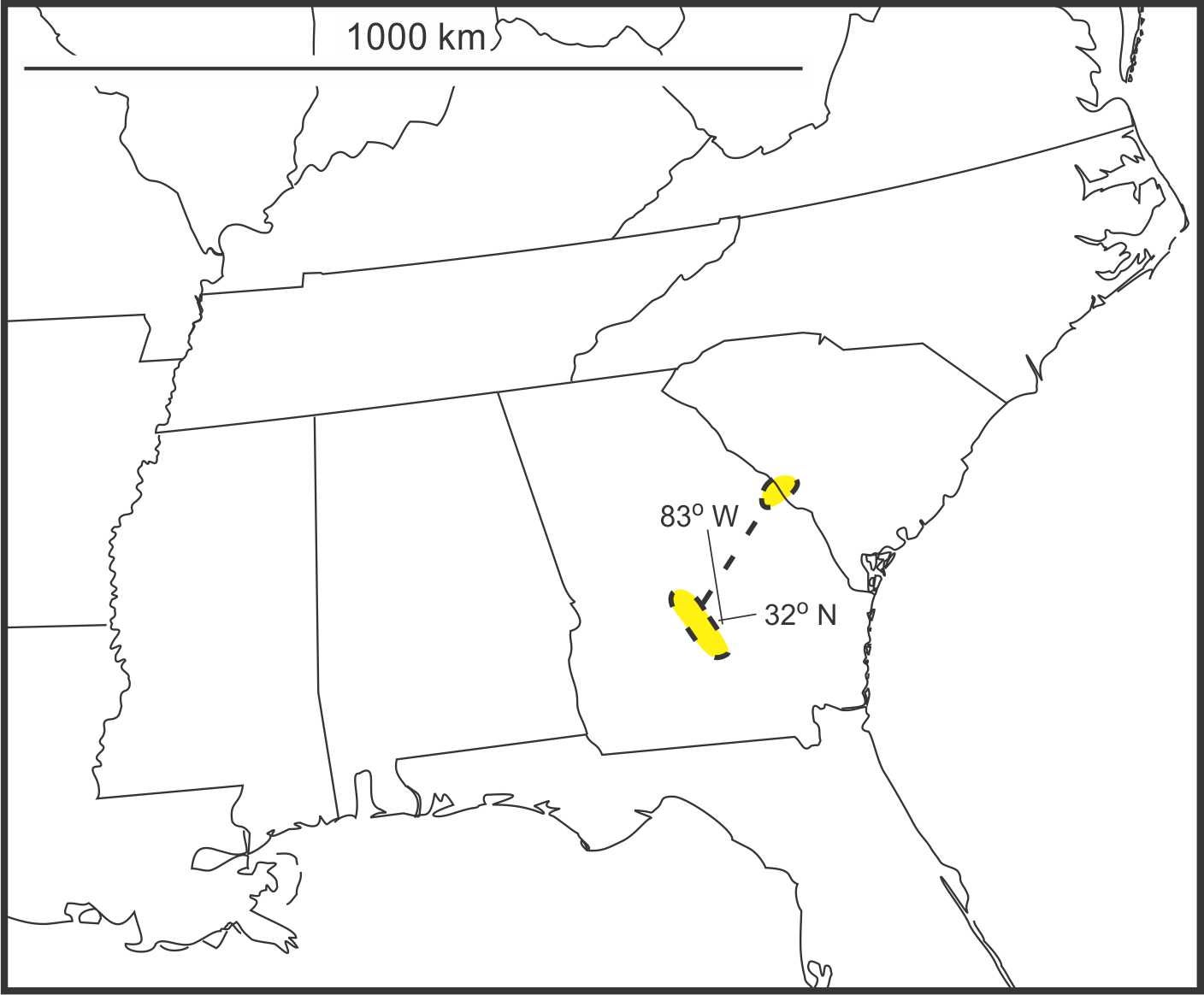
Solidago kralii Semple is native to sandy soils and can be locally common in scattered populations on in south central Georgia and near Augusta, Georgia and adjacent South Carolina. The species is named for Robert Kral. See Semple & Cook (2006 FNA) for a detailed description. Solidago kralii is slightly resinous over much of the plant and especially on the phyllaries, has multiple peduncle bracts, and broader leaves than S. plumosa. It can form dense populations in some places and be very rare in others. The species was first described in 2003. Solidago kralii is diploid (2n=18) throughout its range (Peirson et al. 2012). Semple and Cook (2022) published cytogeography maps for S. kralii and related species.
Solidago kralii was included in the DNA study of S. subsect. Humiles (Peirson et al. 2013). In the polygenomic DNA study of Solidago (Semple et al. 2023), S. kralii came out at the base of a clade that included S. jejunifolia, S. pallida, S. rigidiuscula, and S. plumosa and that was the sister clade to one including S. erecta and S. speciosa).
Semple et al. (2019) presented a multivariate analysis of all 13 species included in S. subsect. Humiles at that date. Solidago kralii was included in the analyses with 12 and 11 species (82% and 82% correct placment a posteriori) and in the analysis of the four species native to the southeastern US (70% correct placment a posteriori). Semple and Beck (2021) placed S. kralii in subsect. Erectae of S. sect. Erectae.
Semple, J.C. 2003. New names and combinations in goldenrods, Solidago (Asteraceae: Astereae). Sida 20(4): 1605–1616.
Peirson, J.A., A.A. Reznicek, & J.C. Semple. 2012. Polyploidy, speciation, and infraspecific cytotype variation in goldenrods: the cytogeography of Solidago subsection Humiles (Asteraceae: Astereae) in North America. Taxon: 61: 197-210.
Peirson, J.A., C.W. Dick and A.A. Reznicek. 2013. Phylogeography and polyploid evolution of North American goldenrods (Solidago subsect. Humiles, Asteraceae). J. Biogeography. 40: 1887–1898.
Semple, J.C., K. Kornobis, A. Mazzorato, G.S. Ringius, and J.A. Peirson. 2019. A multivariate morphometric analysis of Solidago
subsect. Humiles (Asteraceae: Astereae). Phytoneuron 2019-25: 1–61.
Semple, J.C. and R.E. Cook. 2022. The cytogeography of Solidagosect. Erectae, sect. Villosicarpae, sect. Squarrosae, and sect. Brintonia (Asteraceae: Astereae). Taxonomy 2: 261–278.
Semple, J.C., McMinn-Sauder, H., Stover, M., Lemmon, A., Lemmon E., and J. B. Beck. 2023. Goldenrod herbariomics: Hybrid-sequence capture reveals the phylogeny of diploid Solidago. Amer. J. Bot. 110(7): e16164.https://doi.org/10.1002/ajb2.16164
Last revised 18 May 2025 by J.C. Semple
© 2025 J.C. Semple, including all photographs unless otherwise indicated
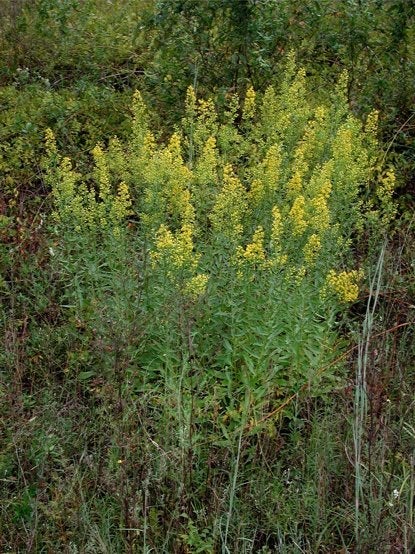
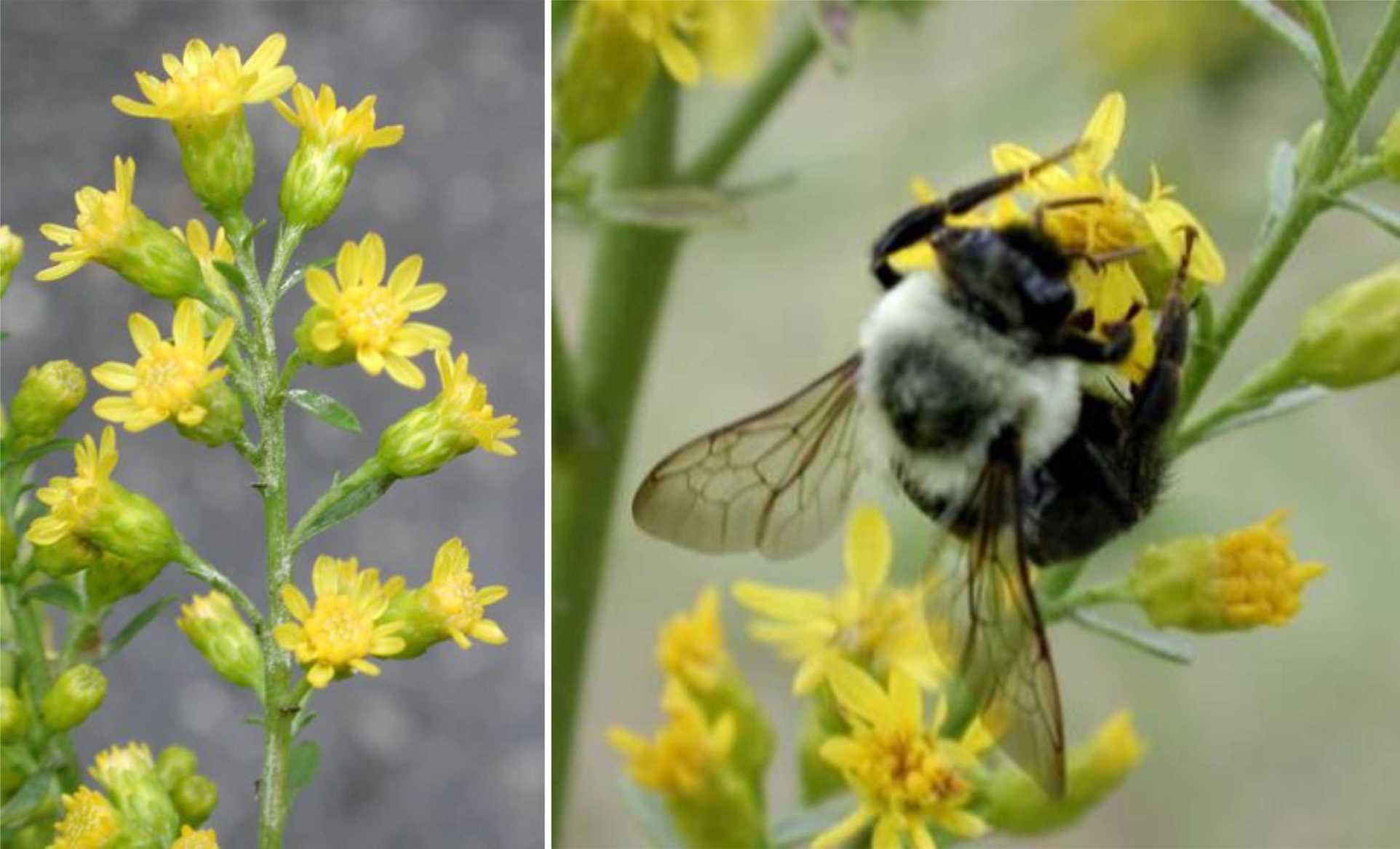
1-6. Solidago kralii. 1. Habitat along fence row, Semple & B. Semple 11208, Pulaski Co., Georgia. 2. Robust plant, Semple & B. Semple 11217, Richmond Co., Georgia. 3. Stems and leaves, Semple et al 2019 Fig 10. 4. Heads, large bee pollinator, S & S. 11208. 5. Heads, phyllaries, fruit body Semple et al 2019 Fig 10. 6. Range map.