Design Team Members: Carmen Lai, Jessica Poon, Sarah Widjaja
Supervisor: Paul Fieguth
Background
Ontario's demand for electricity has been increasing significantly since 1958 as shown in Figure 1.[Reference 1] Ontario is forecasted to reach its energy generation capacity within seven years if no action is taken. When the capacity is reached additional generation plants will be needed to meet these demands during peak hours. The installation and operation of additional plants will result in increased costs for electricity production and adverse environmental impacts. In order to prevent this situation, drastic measures such as shifting energy usage away from peak hours, also known as load-shifting, are required.
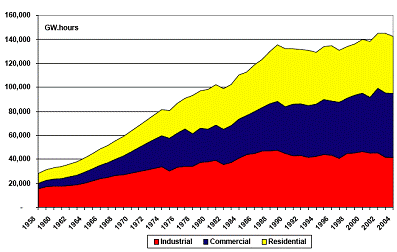
Figure 1 : Electricity demand in Ontario, 1958 - 2004.[Reference 1]
The Ontario Energy Board implemented a smart meter program to provide customers with daily electricity consumption information to encourage them to control their electricity usage patterns. As a result of the smart meter program, a regulated price plan was developed to correspond to the electricity demand fluctuations throughout a day depending on the season as shown in Table 1.[Reference 2] By shifting the amount of energy used in expensive peak hours to cheaper off-peak hours, consumers can reduce their total energy costs. The concept of load shifting can be applied to appliances that do not necessarily need to be running constantly, such as to refrigerators and freezers.
Table 1 : Ontario regulated price plan for electricity consumption starting November 2007.
Day of the Week |
Time |
Time-of-Use
|
Time-of-Use
| |
|
Weekends
&
holidays
|
All
day
|
Off-peak
|
3.0
| |
|
Summer Weekdays (May 1st - Oct 31st) |
7:00
a.m.to
11:00
a.m.
|
Mid-peak
|
7.0
| |
|
11:00
a.m.
to
5:00
p.m.
|
On-peak
|
8.7
| ||
|
5:00
p.m.
to
7:00
a.m.
|
Mid-peak
|
7.0
| ||
|
10:00
p.m.
to
7:00
a.m.
|
Off-peak
|
3.0
| ||
|
Winter Weekdays (Nov 1st - Apr 30th) |
7:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. |
On-peak |
8.7 | |
|
11:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. |
Mid-peak |
7.0 | ||
|
5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. |
On-peak |
8.7 | ||
| 8:00 p.m. to 10:00 p.m. |
Mid-peak |
7.0 | ||
|
10:00 p.m. to 7:00 a.m. |
Off-peak |
3.0 |
Project description
The goal of our project is to shift the electricity usage for residential loads such as refrigerators, freezers and air conditioners from peak hours to off peak hours when the electricity demand is lower. Characteristics of the appliance are gathered through external sources and used for calculating an optimized load-shifting scheme. The optimized load-shifting scheme determines when the appliance should be "on" and when it should be "off” and it is executed through hardware implementation. The success of the load shifting scheme implementation is evident through a reduction in the overall electricity cost for the appliance.
Design methodology
The following methodology is used to accomplish the goals of this project:
1. Perform literature review on household appliances that can be load-shifted.
2. Perform experimental data collection for chosen appliance.
3. Establish requirements and constraints.
4. Generate potential mathematical models to represent the optimization problem.
5. Evaluate and select an appropriate mathematical model.
6. Devise an algorithm that solves the optimization problem.
7. Test and evaluate the load-shifting scheme computed by the algorithm for a variety of appliances.
8. Execute the load-shifting scheme using hardware implementation.
9. Test and evaluate the functionality of the hardware implementation.
References
[1] ICF Consulting, 2005. Electricity Demand in Ontario – A Retrospective Analysis. (PDF)
[2] Ontario Energy Board. Regulated Price Plan – Time of Use Prices. November 5, 2007. (PDF)