If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
The trend in technology today is decreasing the size of electronic devices while increasing their efficiency and performance. Inventing Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor (CMOS) technology was one of the main headways to miniaturize integrated circuits. Nonetheless, it seems that this technology is saturating. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology, on the other hand, is a newly developed technology that has many advantages, and in some cases, is a complementary method for CMOS technology. By combining MEMS with the transistor scaling predicted by Moore's Law, entirely new microsystems can be created which make it possible to squeeze more functionality into a smaller footprint. The advancement in electronic technologies have significantly reduced the power consumption of electronic devices[1, 2] This advancement has created a need for micro-generators because of their small size and long life time compared to batteries[3]. Motion-driven micro-generators are especially popular due to the abundance of vibrations as an ambient natural source [1]. There are two different transduction mechanisms that can bush to convert motion into electrical energy: electromagnetic, which induces current flow from a magnetic field, and electrostatic, which use a variable capacitor structure or piezoelectric materials.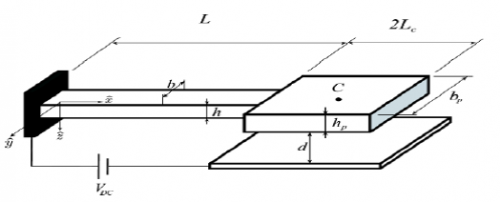
Figure 1: Micro-Power Generator
If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
Contact Waterloo Cases in Design Engineering
Steve Lambert
Tel: (519) 888-4728
Email: steve@uwaterloo.ca
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.