If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
Air pollution, global warming and the need for sustainable energy has intensified the need for efficient, green-energy powered vehicles. There are a number of transportation solutions that have been developed to tackle this issue including the Segway Personal Transporter (PT), a one person dynamically self-balancing transportation vehicle. The Segway PT, designed by Dean Kamen, is a compact vehicle meant to revolutionize the way that short distance travel is conducted. A Segway is much more energy efficient than a traditional car and can transport a rider for a full day on a battery charge worth $ 0.50 of electricity. The Segway’s motion and speed are controlled by the rider shifting their weight forward and backward, and using the handlebar for turning. Although it has never been commercially successful on a large scale, the Segway has been embraced by several groups such as police departments, military bases, warehouses, corporate campuses and industrial sites who use Segway PT to patrol events or facilities. The Segway is also quite popular in the tourism industry as a means to take groups of tourists on guided tours around a city. As a more environmentally friendly transportation method in metropolitan areas, some of the most important design considerations are flexibility, safety and performance.
Chris McClellan, a Mechatronics Engineer at the University of Waterloo, realized that it was an ideal application of control theory. He designed a scaled Segway to create an apparatus that could be used as a common thread in various undergrad courses as a demonstration and/or lab.
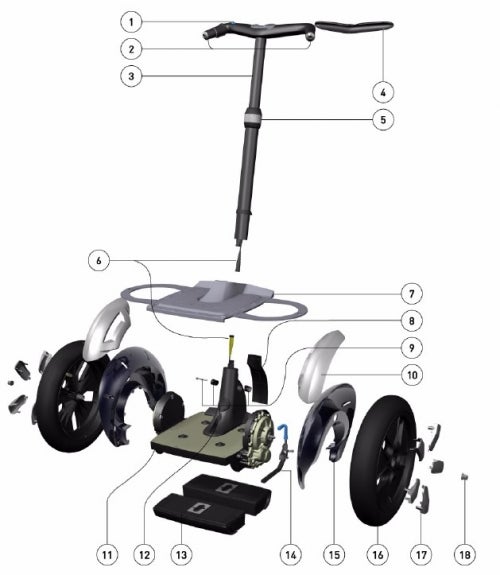
Exploded Segway PT view
This case study explores the design of a self-balancing, battery-powered transportation machine. The purpose of this case study is for students to gain a deeper understanding of interesting electromechanical systems.
If you would like to see more information on this case study, click here!
You can request this case study and a WCDE staff member will get back to you.
Contact Waterloo Cases in Design Engineering
Steve Lambert
Tel: (519) 888-4728
Email: steve@uwaterloo.ca
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg, and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations.