Wednesday, May 7, 2025
SIN Bin: 90
By Department Faculty
Problem
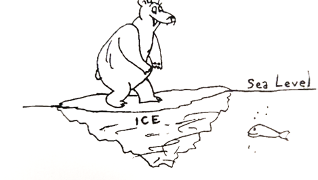
A polar bear, of mass 1250kg, sits at rest on a flat-topped chunk of ice floating as shown with its top at water level (bearly submerged??). The density of the ice is 925 kg/m3 and the density of the water is 1030 kg/m3. (After all it is salt water, silly!). Calculate the mass of the chunk of ice. Provide your answer in kg.
- 41,700
- 27,200
- 15,400
- 11,000
- 9,600