Grant Recipients
Daniel Henstra, Political Science
Evalyna Bogdan, Political Science
Nadine Ibrahim, Civil and Environmental Engineering
Heather Murdock (Research Associate)
Shaieree Cottar (Research Associate)
Sina Golchi (Research Associate)
(Project Timeline: May 2021 - April 2022)
Description
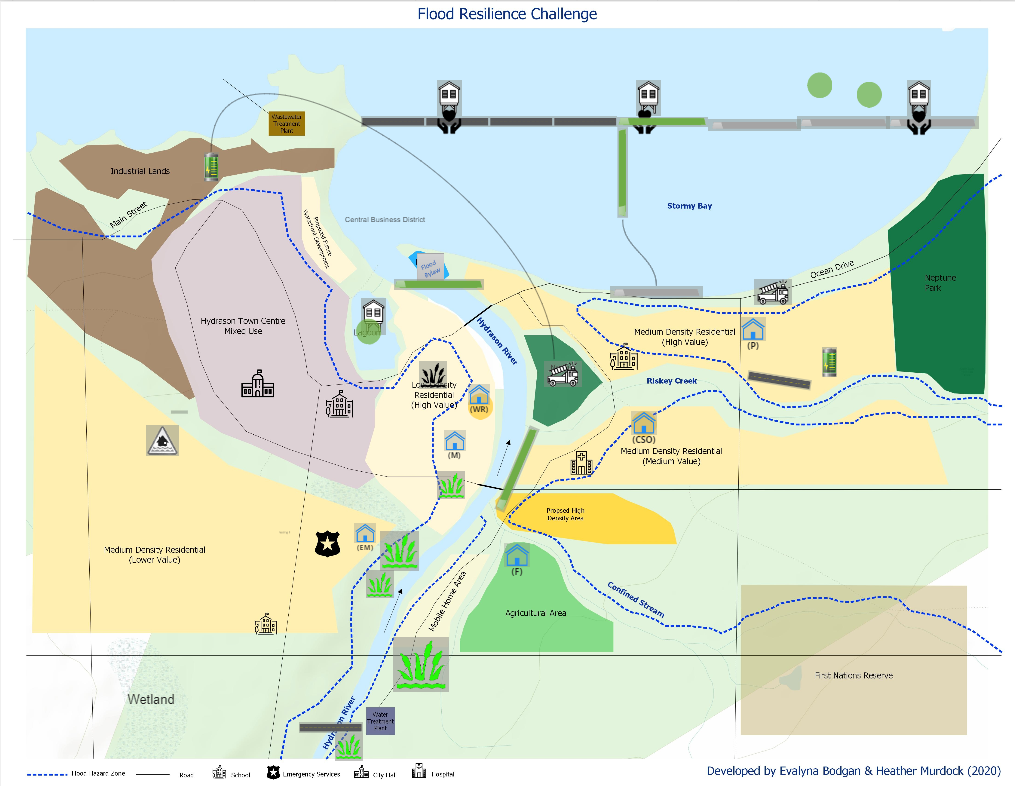
- Flooding is one of Canada’s costliest and most frequent disasters, however, traditional engineering approaches do not adequately address flooding problems. Engineering students lack sufficient training for understanding complex socio-environmental problems and have limited opportunities to gain skills in working collaboratively to address such problems.
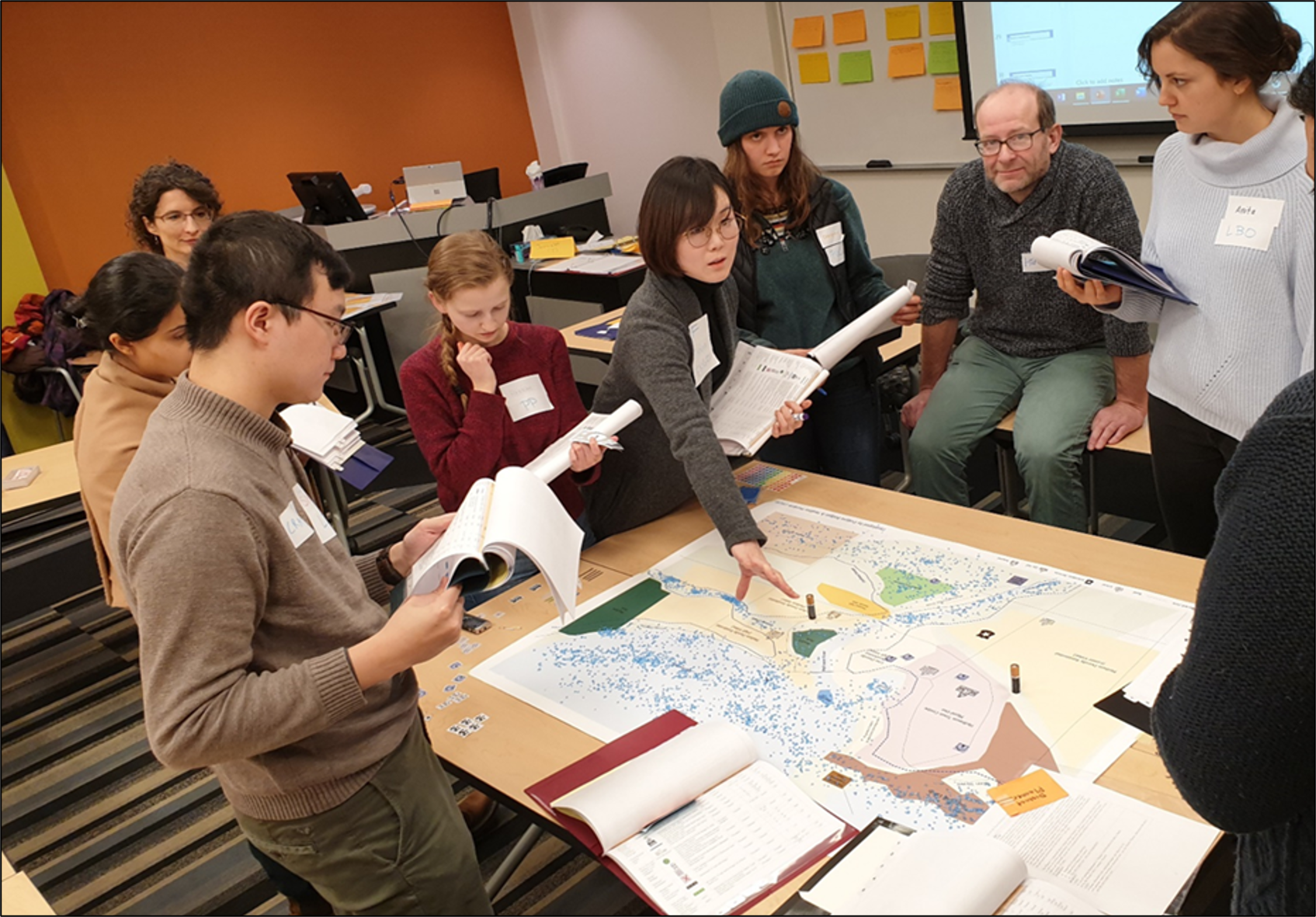
- An experiential learning opportunity is proposed as a 3-hour Flood Resilience Challenge (FRC) role-playing game for students in a third-year engineering course (cross-listed, available to students from multiple disciplines) at the University of Waterloo (UW). To foster deep learning for students, the FRC game seeks to promote a better understanding of the complexity of flooding issues (i.e., governance, risk management) as well as enhance their interpersonal and communication skills. The LITE research project will investigate the effectiveness of the FRC game as an online teaching and learning tool in the context of a large classroom (100+ students), including multiple disciplines, and the University of Waterloo learning environment.
Research Question
- How effective is the online FRC game as a teaching and learning tool in a large versus small class and across multiple disciplines?
Research Objectives
- Investigate the effectiveness of the FRC in promoting experiential learning.
- Conduct a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of the online FRC game in a small classroom (20 students) and a large classroom (100+ students).
Findings
- The differences between the small and large classrooms and disciplines were found to be relatively minor. Brock students were initially more confident than UW students on several measures but then less confident post-game survey, likely because they realized the complexity of the flooding issues. UW engineering students made more comments about the FRM measures than Brock water management students (e.g., would be helpful to know the effectiveness of each type of FRM measure such as how far the protection extends etc.; frustration with some of their peers not having read up on the FRM measures).
- Many of the differences between the small and large classroom were related to logistics of incorporating and running the game which is discussed in the UW T&L May 2022 presentation.
- We conclude that the FRC game is successful in building capacity in flood risk governance by increasing understanding of flooding issues and stimulating discussion. The FRC game can be played in any course on complex socio-environmental problems because the learnings related to complexity, collaboration, conflict, and communication apply to a range of issues. For more details, see Appendix 1.
Dissemination and Impact
- Listed below are some testimonials from students and colleagues who played the FRC game and found it to be a beneficial addition to the course:
- Social learning – importance of iteration: “I think it was beneficial to play three rounds of the game to get a feel for how everything worked” – Brock University, 2022
- Game provides insight into reality: “Game is realistic, forces you to think in a different perspective” - Brock University, 2022
- Diverse stakeholder representation: “Appreciated having the Indigenous reserve in water management is really important, forces us to think about the broader population and the impacts that it will have on others” - Brock University, 2022
- Awareness about climate change issues: “The game increased the level of motivation to learn more about this topic but it did not push me to study this topic but instead take time to make myself more aware about it in this context of the current day” - UW Student, 2022
- Importance of equitable collaboration: “Value of coalitions and collaborators, the more you can unite and find a common ground and having a bigger voice can lead to being heard, build more equity in funding programs” - UW Student, 2022
- The FRC team delivered the following conference and teaching presentations.
- “The Flood Resilience Challenge serious game as an online teaching and learning tool across multiple disciplines and class sizes.” Teaching and Learning Conference, University of Waterloo (online), April 27-28, 2022.
- “Flood Resilience Challenge game: From serious games to real-world scenarios.” Turkstra Talks Speaker Series, Faculty of Engineering, University of Waterloo (online), December 3, 2021.
- Special Session: Water and Cities: Get in the Game! International Symposium on Technology and Society (ISTAS21), University of Waterloo, University of Guelph, and IEEE online. Oct. 27-31, 2021.
- Flood Resilience Challenge Serious Game, Regional Public Works Commissioners of Ontario, Climate Change Committee (online), November 2021.
- The FRC game was implemented for public servants from the Regional Public Works Commissioners of Ontario’s Climate Change Committee. Many participants noted the value of the game and the parallels it drew to some of the challenges that public officials have in balancing the interests of regional government and navigating broader flood risk management priorities.
- 2022 Bogdan, E. A. & Ibrahim, N. The Flood Resilience Challenge serious game as an online teaching and learning tool across multiple disciplines and class sizes. Congress of the Humanities and Social Sciences, CSA, online. May 12-20, 2022.
- 2021 Bogdan, E. A. & Murdock, H. “Enhancing flood risk governance and resilience with a serious role-playing game as an educational and engagement tool.” FloodRisk 2020 (postponed due to COVID), online. June 21-25. INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 2021 Bogdan, E. A. “Enhancing flood risk governance and resilience with a serious role-playing game.” Congress of the Humanities and Social Sciences, CSA, online. May 31-June 4.
- 2020 Murdock, H. & Bogdan, E. A. “Engagement and games: Serious gaming for climate adaptation.” Adaptation 2020, Vancouver, BC. February 19-21.
References
Bots, P., & Van Daalen, E. (2007). Functional design of games to support natural resource management policy development. Simulation & Gaming, 38(4), 512–532.
Fustik, V., Rogleva, N. K., & Petrova, N. (2019). Gamification for practical engineering education in project and risk management [Conference proceeding]. IEEE EUROCON 2019 18th International Conference on Smart Technologies, Novi Sad, Serbia, pp. 1–4.
Flood, S., Cradock-Henry, N. A., Blackett, P., & Edwards, P. (2018). Adaptive and interactive climate futures: Systematic review of ‘serious games’ for engagement and decision-making. Environmental Research Letters, 13(6), 063005.
Flyvbjerg, B., Landman, T., & Schram, S. (2012). Introduction: New directions in social science. In B. Flyvbjerg, T. Landman, & S. Schram (Eds.), Real social science: Applied phronesis (pp. 1–14). Cambridge University Press.
Gilbert, B. L., Banks, J., Houser, J. H. W., Rhodes, S. J., and Lees, N. D., (2014). Student development in an experiential learning program. Journal of College Student Development, 55(7), 707–713.
Hanson, L. L., & Kahane, D. (2018). Introduction: Advancing public deliberation on climate change and other wicked problems. In L. L. Hanson (Ed.), Public deliberation on climate change (pp. 3–32). Athabasca University Press.
Haque, C. E., Kolba, M., Morton, P., & Quinn, N. P. (2002). Public involvement in the Red River Basin management decisions and preparedness for the next flood. Global Environmental Change Part B: Environmental Hazards, 4(4), 87–104.
Innes, J. E., & Booher, D. E. (2003). Collaborative policymaking: Governance through dialogue. In M. A. Hajer & H. Wagenaar (Eds.), Deliberative policy analysis: Understanding governance in the network society (pp. 33–59). Cambridge University Press.
Kamaruzaman, F. M., Hamid, R., Mutalib, A. A. (2017). A review on issues and challenges in incorporating complex engineering problems in engineering curriculum and proposed solutions[Conference proceeding]. 2017 7th World Engineering Education Forum (WEEF), Kuala Lampur, Malaysia, pp. 697-701.
Klijn, F., Knoop, J. M., Ligtvoet, W., & Mens, M. J. P. (2012). In search of robust flood risk management alternatives for the Netherlands. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 12, 1469–1479.
McCarthy, D. D., Crandall, D. D., Whitelaw, G. S., General, Z., & Tsuji, L. J. (2011). A critical systems approach to social learning: Building adaptive capacity in social, ecological, epistemological (SEE) systems. Ecology and Society, 16(3), 18.
McGillivray, G. (2016, January 18). Flood governance in Canada: Who’s minding the store? [Online article]. Canadian Underwriter.
Mndzebele, S., & Mckenna, S. (2013). Applying a student curriculum discourse in higher education teaching and learning. Africa Education Review, 10(1), 1–17.
Moser, S. (2012). Getting real about it: Navigating the psychological and social demands of a world in distress. In D. R. Gallagher, R. N. L. Andrews & N. L. Christensen (Eds.), Sage handbook on environmental leadership (pp. 432–440). Sage.
Powers, R. (2020, November). Unit 4 Week 11: Proposing Change. Traditional Organizational Change Theory. Athabasca University Survey of Current Educational Technology Applications Moodle:
Rittel, H. W., & Webber, M. M. (1973). Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sciences, 4(2), 155–169.
Rodela, R., Cundill, G., & Wals, A. E. (2012). An analysis of the methodological underpinnings of social learning research in natural resource management. Ecological Economics, 77, 16–26.
Salvini, G., Van Paassen, A., Ligtenberg, A., Carrero, G. C., & Bregt, A. K. (2016). A role-playing game as a tool to facilitate social learning and collective action towards Climate Smart Agriculture: Lessons learned from Apuí, Brazil. Environmental Science & Policy, 63, 113–121.
Shrubsole, D. (2013). A history of flood management strategies in Canada revisited. In E. C. H. Keskitalo (Ed.), Climate change and flood risk management: Adaptation and extreme events at the local level (pp. 95–120).Edward Elgar.
Sörensen, J., Persson, A., Sternudd, C., Aspegren, H., Nilsson, J., Nordström, J., . . . Mobini, S. (2016). Re-thinking urban flood management—time for a regime shift. Water, 8(8), 332.
Surry, D. & Farquhar, J. (1997). Diffusion theory and instructional technology. Journal of Instructional Science and Technology, 2(1).
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction. (2009). UNISDR terminology on disaster risk reduction.
University of Waterloo. (2008). Academic Program Reviews: Undergraduate Degree Level Expectations.
University of Waterloo. (2011). The Task Force on Innovative Teaching Practices to Promote Deep Learning at the University of Waterloo: Final Report.


